Author: Victor Medina & Mike Eberle | December 21, 2022
Summary
Many users of Legacy C-8 Aqueous Film Forming Foams (AFFF) are considering changing to foams to minimize release of PFOA, PFOS and 8:2 FTS. Modern C-6 AFFF and fluorine free foams (FFF) are replacement options. FFF is preferable from an environmental perspective, but current FFF formulations are inferior in firefighting characteristics to legacy C-8 AFFF and modern C-6 AFFF. In replacing the legacy C-8 foam, equipment decontamination is recommended. The process should be carefully planned and PFAS contaminated residuals properly managed.
Background
Legacy (AFFF) used for firefighting are a significant source of poly-, perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in the environment. Key PFAS from these foams are discussed below:
- Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS), which are long-chain C8 PFAS, have been the initial focus of regulatory criteria setting and some states have enforceable drinking water standards ranging from 8 to 70 nanograms per liter (ng/L). In 2022, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) issued lifetime drinking water health advisories of 0.0004 and 0.020 ng/L for PFOA & PFOS, respectively, and the EPA is expected to propose enforceable maximum contaminant levels (MCLs) for PFOA and PFOS in the near future.
- 8:2-fluorotelomer sulfonate (8:2 FTS) is another long-chain C-8 PFAS that is currently not regulated in drinking water but readily transforms into PFOA.
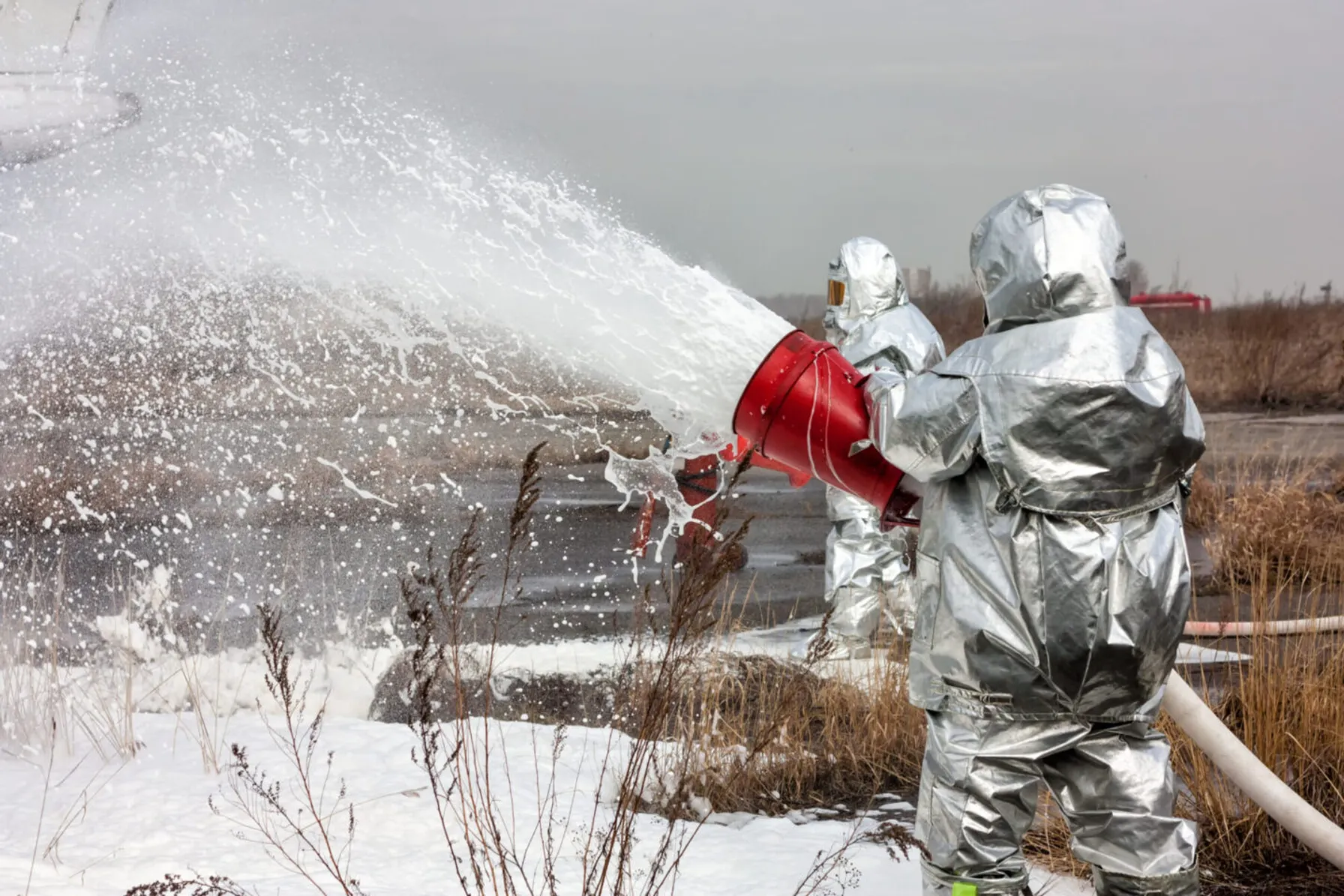
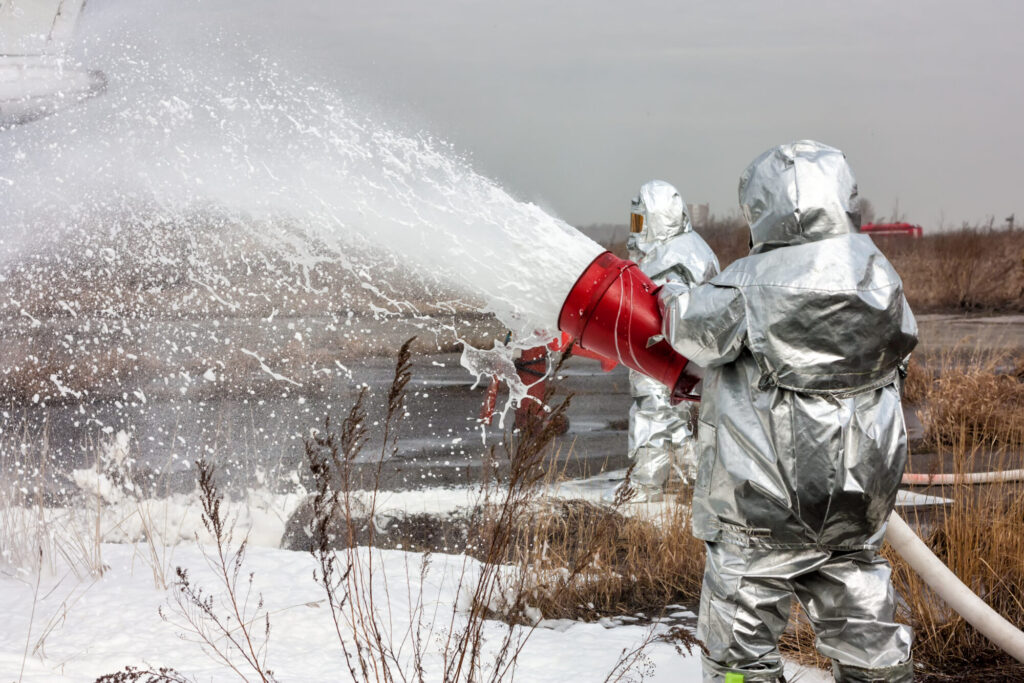
AFFF is applied to fires via firefighting equipment. This includes fire extinguishers, firefighting vehicles and fixed systems (e.g., foam gun systems used to contain fires around tanks and fuel storage areas and foam dispersing systems). AFFF concentrate is placed in these devices and foam is generated by mixing the concentrate with water/air under pressure using specialized nozzles.
With current and expected regulation, many entities are exploring the process to replace their legacy AFFF (C-8) with other short-chain AFFF (C-6 fluorotelomer sulfonates) or fluorine free foams (FFF). This requires removal of the legacy AFFF and decontamination of the firefighting equipment. Cost analyses indicate that it is generally much less expensive to decontaminate firefighting equipment than it is to replace it. However, some replacement foams may differ in density/viscosity, which may require replacement of pumps, valves and/or nozzles, which would increase the decontamination costs. Very small systems and fire extinguishers would likely be less expensive to simply replace.
TRC reviewed processes and data from industrial decontamination efforts and papers/reports and studied research conducted by the Department of Defense Strategic Environmental Research & Development Program/Environmental Security Technology Certification Program (SERDP/ESTCP) to develop recommendations.

Legacy AFFF Properties
Properties of legacy AFFF that make it very effective for fire suppression include:
- The ability of the AFFF to form a thin, but stable, film on the water interface that smothers the fire. This film also prevents reignition
- Viscosity and density similar to water, allowing for easy pumping and dispersal
Replacement Foams
There are two options available to replace legacy AFFF concentrate. (1) Modern Fluorotelomer AFFF, also called C-6 foam, uses short-chain fluorotelomer sulfonates and (2) Fluorine Free Foams (FFF) that use a variety of fluorine free organic surfactants. The table below compares these replacement options and legacy AFFF.
| Replacement Foams Versus Legacy AFFF | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | C-8 Legacy AFF | Modern C- 6 AFFF | FFF |
| Environmental Concerns | High environmental concerns. Contains PFOA/PFOS or compounds that may transform to these compounds. | Uncertain environmental concern. Does not contain or transform to PFOS/PFOA. Can transform to perfluoroheptanoic acid (PFHpA) that is regulated in several states. | Very little environmental concern associated with PFAS but foam contains higher concentrations of hydrocarbon surfactants that could pose a risk if released to surface water. Overall concerns much lower than C-8 Legacy or C-6 AFFF. |
| Effectiveness of Suppressing Fuel/ Chemical Fires | Excellent | Comparable to C-8 Legacy AFFF | Inferior to C-8/C-6 foams |
| Ability of Foams to Prevent Fire Reignition | Excellent | Comparable to C-8 Legacy AFFF | Inferior to C-8/C-6 foams |
| Compatibility of Foams with Existing Firefighting Equipment | Fully Compatible | Highly compatible. Similar density and viscosity to C-8 Legacy AFFF |
Low compatibility. Most have high viscosity and greater density. Existing pumps, valves and nozzles may need to be replaced. |
From an environmental perspective, FFFs are preferential because of the uncertainty of the toxic characteristics of shorter chain C-6 PFAS compounds. In terms of fire suppression, modern C-6 fluorotelomer AFFF performs comparably to that of the C-8 legacy foams. FFFs may have utility for sites with isolated chemical fire hazards where longer extinguishing times are acceptable. However, most chemical fires will require replacement foams with extinguishing characteristics that C-6 fluorotelomer foams exhibit. There is substantial investment into the development of FFF, so it is possible that improved products will be available in the future. When switching foams, check for compatibility to existing pumps, valves and nozzles.

Learn More From Our Technical Experts
TRC’s Center of Research and Expertise (CORE) is a multidisciplinary team led by proven subject matter experts in over 30 specialized technical areas. Our monthly CORE newsletter shares valuable insights on emerging technologies, significant challenges and innovative solutions present in many industries across the world. Our experts also share how they use their unique skills and experience to solve client issues and support our communities and the environment.
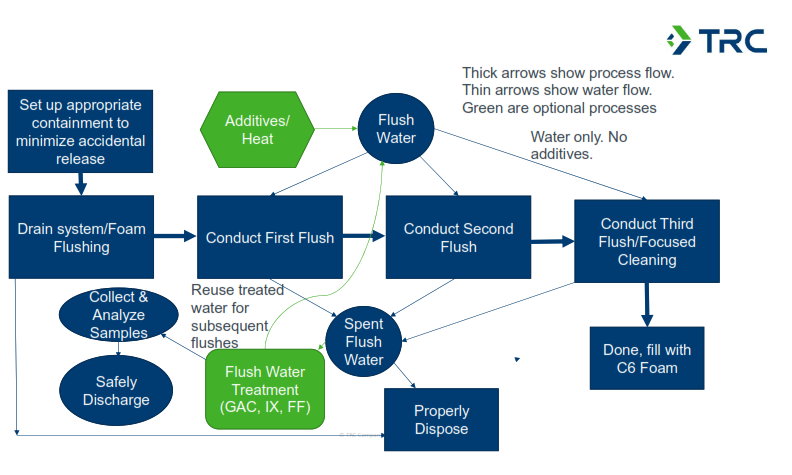
Foam Removal and Decontamination
Foam removal and decontamination should be carefully planned. This includes estimating waste volumes (AFFF concentrate, flushes and rinsates), worker protection, sufficient storage capacity for residuals, leak minimization processes and eventual management and disposal of collected residuals.
The first step for replacement is removal of the legacy foam from the equipment. The foam can be removed via drains at low points in the system, and the removal should be carefully managed to minimize accidental releases.
There are currently no existing requirements for the decontamination of firefighting equipment at the federal level. TRC recommends that decontamination be conducted because residual C-8 foam in the system could result in mixing with the replacement foam and the subsequent release of C-8 PFAS to the environment when the new foam is applied. After draining the entire system of AFFF concentrate:
- Conduct a foam flush, which is a rinse, or series of rinses, until foaming is no longer found in the rinsate.
- Remove and replace disposable elements like bladders and hoses.
- Consider conducting detailed, focused cleaning of valves, elbows, flanges and other elements that may be resistant to the flushing process or removing and replacing these.
- Conduct triple or quadruple rinse to remove the majority of legacy PFAS contaminants. Each rinse should recirculate from 45 minutes to 1 hour before discharging and collecting.
- The foam flush and rinsate water could be treated onsite to reduce the volume needed for disposal. Potential treatments include granular activated carbon (GAC), ion exchange (IX) or foam fractionation (FF).
- Take care to minimize any leaks or accidental releases of the foam flush/rinsate. Collected rinsates should be stored with secondary containment prior to treatment or disposal.
- Laboratory analysis of the final rinsate is an option, but is often not practical because of the need to return the firefighting equipment to service. Further, there are no established standards or advisories to meet.
- Contaminated residuals (AFFF concentrate, rinsates, spent treatment media, etc.) should be managed appropriately.
Studies have shown that legacy PFAS can partition on surfaces in the firefighting equipment, including stainless steel materials. These can be released over time, causing “rebound.” If this is a concern, consider the following:
- Commercially available additives can be used to improve the AFFF decontamination.
- Solvents like methanol/ethanol or non-foaming surfactants could also be used to enhance decontamination efficiencies, although added solvents must be considered in the evaluation of disposal options.
- For legacy C-8-based foams, heated water can be used to improve the mass transfer from the surfaces to the rinsate water.
Flushing Process Options

Disposal of Residuals
Responsible disposal of the residuals should be conducted. As part of the planning process, discussed in the Foam Removal and Decontamination section, volumes of residuals should be estimated as part of the planning process and these estimates can be used to estimate disposal costs. Approaches for residuals management include incineration and landfilling with onsite methods under development. TRC can assist with making appropriate selections.
How Can TRC help?
If changeout of C-8 foam is desired, then TRC can assist in recommending a suitable foam replacement and develop plans for foam removal and equipment decontamination. TRC can assist in finding a quality contractor to conduct the foam removal and equipment decontamination and can develop plans to manage residuals from legacy foam removal and equipment decontamination. Contact our experts below to learn more.
Sharing Our Perspectives
Our practitioners share their insights and perspectives on the trends and challenges shaping the market.

Changes to EPA’s Risk Management Program (RMP) Regulations Are Coming
April 14, 2023
Changes to the Risk Management Program (RMP) regulations were signed into a final rule on February 27, 2024, by EPA Administrator Michael S. Regan.

EPA Finds Trichloroethylene Presents Unreasonable Risk in Final Risk Evaluation
April 6, 2023
On Jan 9, 2023, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) revised the Toxic Substance Control Act (TSCA) to reflect a new risk determination for trichloroethylene (TCE).

Proposed Use of a Hazard Index for PFAS National Primary Drinking Water Regulation (NPDWR)
April 4, 2023
The Proposed MCL and MCLG for the four PFAS, PFNA, PFHxS, GenX, and PFBS, considers their toxicity as additive. The EPA has proposed a HI of 1.0 as the MCL and MCLG for the four PFAS combined.

Using the R2 Guidance in Indiana
March 21, 2023
TRC outlines the new R2 Guidance in Indiana

Routinely Evaluating the Health & Effectiveness of Integrated Systems to Manage EHS/ESG Risks – Part I
March 1, 2023
Once established, an EHS/ESG management system must be routinely evaluated to ensure it remains effective to identify and control risks, as well as accommodate and adjust for changes that occur to/within the organization.

Consequences of a Lowered NAAQS for PM2.5
February 16, 2023
TRC breaks down the significance of EPA lowering the NAAQS for PM₂.₅

EPA Announces $2 Billion in Funding to Address Emerging Contaminants in Drinking Water
February 14, 2023
Environmental Protection Agency Administrator Michael Regan announced $2 Billion in infrastructure funding to help the nation’s rural water supplies.

EPA Publishes Effluent Guidelines Program Plan 15
February 14, 2023
The EPA announced updated effluent limitations guidelines under Plan 15, focusing on the evaluation and rulemaking process for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) discharges.

Phase I ESA ASTM Standard Update: The Wait is Over
December 21, 2022
The USEPA published a Final Rule making the ASTM E1527-21 Phase I ESA standard AAI compliant.

Proactive Enforcement is Key in the EPA FY2022-2026 Strategy
October 19, 2022
A core element of the EPA FY2022-2026 Strategic Plan focuses on environmental compliance.

Preparing for EPA Inspections in Environmental Justice Communities
October 4, 2022
The EPA Office of Enforcement and Compliance Assurance Have Expanded Goals to Strengthen Enforcement and Protections Within EJ Communities

New National Emerging Contaminants Research Initiative
September 12, 2022
The Executive Office of the President of the United States announced a National Emerging Contaminant Research Initiative

NERC Proposes Implementation Guidance for PRC-019-2
August 22, 2022
NERC has proposed implementation guidance for PRC-019-2, the standard that verifies coordination of generating unit facility or synchronous condenser voltage regulating controls, limit functions, equipment capabilities and protection system settings.

Optimizing EHS/ESG Information Management and Reporting Systems by Leveraging Innovative Digital Technology Solutions
August 10, 2022
A single, integrated enterprise wide EHS/ESG IMS can significantly improve performance and communicate progress towards organizational requirements and goals.

Revisions to FAC-001 and FAC-002 Submitted for FERC Approval
July 12, 2022
Reliability Standards FAC-001-4 and FAC-002-will resolve uncertainty regarding the meaning of “materially modify” under the currently effective standards.

FERC Order No. 881-A Has Implications for NERC Compliance Programs
June 23, 2022
Updated Order will have significant impact on NERC compliance programs related to both PRC standards and facilities ratings. Utilities should review the Order’s requirements and prepare for changes needed to remain compliant.

Integrating Sustainability, Digital Connectivity and Design Optimization in Wastewater Treatment Systems
June 20, 2022
Some organizations rarely think about water and wastewater treatment, until there is a problem. American industry depends on the ability to treat wastewater discharges while complying with regulatory standards and addressing emerging contaminants. If wastewater treatment fails, our environment is negatively impacted, and companies are exposed to shutdowns, delays and fines.

Climate Action and Environmental Justice are at the Forefront of EPA’s Strategic Plan
June 14, 2022
The EPA issued its Fiscal Year 2022-2026 Strategic Plan. Although the strategic plans emphases often change with administrations, we can be reasonably certain that the Plan reflects priorities through 2024.

NERC’s Revised PRC-024-3 Standard for Inverter-Based Generation Effective in October 2022
May 11, 2022
Changes to PRC-024-3 in support of inverter-based generation performance are going into effect in October of this year. Interconnection programs and documentation procedures may need to be updated in order to maintain compliance.

FERC Issues Notice of Inquiry Regarding Dynamic Line Ratings
April 25, 2022
There are significant technical challenges involved in implementing Dynamic Line Ratings in the planning and operation of utility systems. Utilities should be prepared to modify their NERC compliance programs as necessary to address the potential introduction of DLR in their businesses.

Why Are ESG Frameworks Important?
April 13, 2022
ESG standards significantly impact long-term growth, leading many companies to integrate ESG reporting into their corporate social responsibility (CSR) strategies. ESG frameworks are broad and diverse, and establishing a reporting system that covers your industry’s most relevant metrics can be challenging.

EPA Coal Ash Compliance Expectations Updated
March 28, 2022
New EPA Communications highlight new Coal Combustion Residual compliance expectations, a shift from the current program.

New NERC Guidance Supports the Implementation of Grid Forming Inverters
March 8, 2022
NERC has issued a new report highlighting the key attributes of various inverter controls to support proper implementation and to protect reliability.

NERC Recommends Approaches for Underfrequency Load Shedding Programs
February 24, 2022
In a recently released reliability guideline, NERC recommends additional approaches for Underfrequency Load Shedding (UFLS) program design to help utilities effectively consider the effects of Distributed Energy Resources (DERs). The guidance was developed to address the accelerated transition of the power system to locally installed, decarbonized resources that depend on inverters. These new technologies introduce operational controls issues into the electric grid. UFLS data gathering and analysis methodologies may require modification to address reliability risks.

NERC and FERC Recommend Protection System Commissioning Improvements
January 18, 2022
Between 18 and 36 percent of reported utility misoperations were attributed to issues that could have been detected through a properly implemented PSC.

FERC & NERC Issue Joint Report on Freeze Reliability Failures
December 15, 2021
The in-depth report outlines twenty-eight recommendations to address freeze reliability failures, including operating practices and recommendations for NERC standards modifications surrounding generator winterization and gas-electric coordination.

NERC Accelerates Additional Cold Weather Standards Changes
November 22, 2021
At its November 2021 meeting, NERC’s Board of Trustees took aggressive action to advance critical cold weather Reliability Standards. Most notably, the group approved the 2022-2024 Reliability Standards Development Plan, which prioritizes standards projects for the coming years including a resolution to include new cold weather operations, preparedness and coordination standards as high priority development projects.

OSHA’s National Emphasis Program on Heat-Related Illness and Injuries
November 3, 2021
On September 20, 2021 in an OSHA National News Release, OSHA published a memorandum establishing an enforcement initiative that is designed to prevent and protect employees from heat-related illnesses and death. This initiative, which develops a National Emphasis Program (NEP) on heat inspections, is an expansion of an already existing Regional Emphasis Program (REP) in OSHA’s Region VI, which covers Arkansas, Louisiana, New Mexico, Oklahoma and Texas.

New Potential Compliance Standards Identified at FERC Technical Conference on Reliability
October 18, 2021
With a focus on the reliability impact of extreme weather and the shortcomings of current system planning approaches, both NERC and FERC conference participants opened the door to potential forthcoming compliance standard enhancements or changes.

NJDEP Implements New Jersey Environmental Justice Law Through Administrative Order
October 5, 2021
On September 22, 2021, the New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection (NJDEP) Commissioner announced the issuance of Administrative Order (AO) No. 2021-25 to implement New Jersey’s Environmental Justice (EJ) Law. This order is effective immediately, and applicants seeking to site new major source facilities, renew major source permits or expand existing facilities with major source permits (e.g., Title V air permits) in overburdened communities are affected. There are more than 4.5 million people that live within 331 municipalities that are overburdened communities in the state of New Jersey.

OSHA Returns to In-Person Inspections As COVID-19 Restrictions Lift
August 4, 2021
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) is authorized by the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 (OSH Act) to assure employers provide safe and healthful work conditions free of recognized hazards and by setting and enforcing standards and providing training, outreach, education and technical assistance. OSHA has recently announced the return to in-person inspections as COVID-19 restrictions begin to lift.

NERC Proposes Revisions to CIP-008
March 27, 2021
NERC’s CIP-008 standard aims to mitigate reliability risks resulting from a Cyber Security Incident by specifying incident response requirements. Newly proposed revisions would augment mandatory reporting to include incidents that compromise, or attempt to compromise, a utility’s Electronic Security Perimeter (ESP) or associated Electronic Access Control or Monitoring Systems (EACMS).

EPA continues to aggressively address PFAS wastewater with two new strategies
January 4, 2021
EPA takes steps toward PFAS wastewater and storm water permitting, and analytical methods for testing.

Ecological Risk of PFAS from AFFF-Impacted Sites
June 30, 2020
The facts on evaluating exposure to wildlife

Targeting Perfection in the Construction and Operation of Pipelines
October 18, 2019
To have an impact on the delivery or operation of a pipeline, it’s vital to eliminate the intra- and inter-company barriers, including those in the areas of communications, culture and technology.

PHMSA Publishes New Rules to Increase the Safety of Hazardous Liquid Pipelines and Gas Transmission Pipelines
September 25, 2019
The Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration this week published important new rules aimed at improving pipeline safety.

NERC Calls for New Approach to Reliability Planning Due to Gas Supply Disruption Risks
December 14, 2017
A recently published NERC report concludes that as reliance on natural gas to meet electric generation requirements increases, additional planning and operational measures must be considered to mitigate power system reliability risks.

PFAS in Consumer Products: Assessing the Risk of Dermal Exposures
July 17, 2025
Products, such as bandages, baby wipes and feminine care products, may contain trace levels of PFAS due to intentional use or cross-contamination, which has prompted recent concerns about skin absorption and long-term health effects.

TRC’s Webinar On-Demand ART-PFAS Technology
May 7, 2025
TRC’s Nidal Rabah and Brendan Lazar present ART-PFAS, an award-winning in-situ alternative to pump-and-treat for remediating PFAS and VOCs in groundwater.

Treatment of PFAS to Allow for Beneficial Use of Impacted Dredged Sediments
July 18, 2024
Approximately 200 to 300 million cubic yards of sediment are dredged each year by the US Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) and other federal interests (USEPA, 2007).

Coming at You Fast – The Latest on RCRA and PFAS Regulations
March 1, 2024
The EPA published its Proposed Rule for Listing of Specific PFAS as Hazardous Constituents under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA).

New EPA Rule Impacts PFAS TRI Reporting and Supplier Notifications
November 20, 2023
What Affected Facilities Need to Know About Applicability, Reporting Changes and Deadlines

EPA Proposes Changes to Air Emissions Reporting Requirements (AERR)
August 30, 2023
The EPA is proposing updates to their Air Emissions Reporting Requirements (AERR) through amendments to 40 CFR Parts 2 and 51.

How Does PFAS Contamination Impact the Environment?
August 11, 2023
PFAS are widely used in the production of numerous products. Some PFAS chemicals are the by-product of manufacturing processes. As a result, PFAS contamination is widespread, with PFAS being found nearly everywhere in the world.

Helping Airports Identify and Mitigate PFAS Risks
May 30, 2023
This white paper focuses on some unique strategies and situations we have encountered at some airport sites.

EPA Finds Trichloroethylene Presents Unreasonable Risk in Final Risk Evaluation
April 6, 2023
On Jan 9, 2023, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) revised the Toxic Substance Control Act (TSCA) to reflect a new risk determination for trichloroethylene (TCE).

Proposed Use of a Hazard Index for PFAS National Primary Drinking Water Regulation (NPDWR)
April 4, 2023
The Proposed MCL and MCLG for the four PFAS, PFNA, PFHxS, GenX, and PFBS, considers their toxicity as additive. The EPA has proposed a HI of 1.0 as the MCL and MCLG for the four PFAS combined.

Proposed MCLGs and MCLs for PFAS
March 15, 2023
Final Regulatory Determination for Contaminants on the Fourth Drinking Water Contaminant Candidate List

QA and Chemistry Services
February 23, 2023
TRC offers many QA and Chemistry services including data usability assessments, limited and full data validation reports, quality assurance project plan preparation, selection of appropriate analytical methodologies and laboratory audits.

PFAS Fate and Transport
February 23, 2023
Understanding PFAS properties and behavior is key to effective detection and remediation.

PFAS Fate and Transport: Conceptual Site Models
February 23, 2023
The conceptual site model describes site-specific sources, release and transport mechanisms, exposure media, exposure points, exposure pathways and routes and potential human and/or ecological receptor populations.

EPA Announces $2 Billion in Funding to Address Emerging Contaminants in Drinking Water
February 14, 2023
Environmental Protection Agency Administrator Michael Regan announced $2 Billion in infrastructure funding to help the nation’s rural water supplies.

EPA Publishes Effluent Guidelines Program Plan 15
February 14, 2023
The EPA announced updated effluent limitations guidelines under Plan 15, focusing on the evaluation and rulemaking process for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) discharges.

PFAS: Remedial Approaches
February 8, 2023
Remediating Per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from the soil and water requires effective techniques and innovative technologies. TRC’s experts are well versed in several remediation strategies intended to remove PFAS and prevent re-exposure.

TRI PFAS Reporting Requirements Continue to Expand
January 25, 2023
The list of PFAS for TRI reporting has increased to a total of 189 for reporting year 2023.

PFAS Discharges in NPDES Permits
December 19, 2022
In a follow-up to the EPA Office of Water’s April 28, 2022 memo, EPA released “Part 2″, providing guidance for the NPDES permitting/pretreatment program as it relates to restricting discharges of PFAS to water bodies.

Washington State Establishes PFAS Cleanup Levels
September 21, 2022
The Washington State Department of Ecology (Ecology) recently published a list of 6 PFAS compounds that now have soil and groundwater cleanup levels

New National Emerging Contaminants Research Initiative
September 12, 2022
The Executive Office of the President of the United States announced a National Emerging Contaminant Research Initiative

EPA Issues Proposed Rule Designating PFOA and PFOS as Hazardous Substances
September 7, 2022
The EPA has issued a pre-publication version of a proposed rule to designate two PFAS compounds as hazardous substances under CERCLA.

Five New PFAS Added to EPA Regional Screening Levels (RSLs)
June 24, 2022
EPA announced the addition of five new PFAS to the list of Regional Screening Levels (RSLs)

EPA Announces Updated Drinking Water Health Advisories for Four PFAS Chemicals: PFOS, PFOA, PFBS, & GenX
June 24, 2022
On June 15, 2022, the EPA released updated Health Advisory Levels for four per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in drinking water

Integrating Sustainability, Digital Connectivity and Design Optimization in Wastewater Treatment Systems
June 20, 2022
Some organizations rarely think about water and wastewater treatment, until there is a problem. American industry depends on the ability to treat wastewater discharges while complying with regulatory standards and addressing emerging contaminants. If wastewater treatment fails, our environment is negatively impacted, and companies are exposed to shutdowns, delays and fines.

Worst Case Discharges of Hazardous Substances – Proposed Rule
May 25, 2022
In compliance with the Clean Water Act (CWA), the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recently proposed a new rule for onshore non-transportation-related facilities requiring specified facilities to plan for worst case discharges (WCDs) of CWA hazardous substances that could cause substantial harm to the environment.

PFAS Discharges and NPDES Permits
May 25, 2022
On April 28, 2022, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) Office of Water released a memo addressing the use of National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permits to restrict per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) discharges to water bodies.

EPA Proposes Aquatic Life Criteria for PFOA and PFOS
May 25, 2022
On May 3, 2022, under the Clean Water Act (CWA), the United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) proposed the first aquatic life criteria for both short-term and long-term toxic effects from Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid (PFOS).

SEC Releases New Proposed Rules Requiring Public Companies to Disclose Climate Risks
April 12, 2022
On March 21, 2022, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) issued its proposed rules for The Enhancement and Standardization of Climate-Related Disclosures for Investors which would require public companies in the U.S. to disclose information in their annual financial reports.
PFOA & PFOS As CERCLA Hazardous Substances: What Does This Mean and How Can You Be Prepared?
February 17, 2022
A plan to designate two per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) as “hazardous substances” under CERCLA was recently submitted by the EPA.

New Phase I ESA Standard Will Affect Environmental Due Diligence
January 25, 2022
After years of review, revisions and discussions, the new ASTM E1527 Phase I Environmental Site Assessment (Phase I ESA) standard has been published. The new standard includes updates to definitions, clarifications on processes and requirements, and guidance for emerging contaminants.

Fifth Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule Lists 29 PFAS
January 21, 2022
EPA published fifth Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule as required every five years and 29 of the 30 contaminants listed are PFAS.

Need help collecting PFAS samples for NJDEP deadline December 15?
October 7, 2021
NJDES Category B or L Industrial Permit holders – If you haven’t obtained your first PFAS sample yet, time is running out. All New Jersey Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NJDES) Category B or L Industrial Permit holders are required by the New Jersey Department of Environmental Projection (NJDEP) to collect two representative effluent samples, taken 30 days apart, to be analyzed for PFAS by an approved laboratory and submitted to them by December 15, 2021.

Interpretation of “Waters of the United States” (WOTUS) Reverts to Pre-2015 Regulatory Definition
September 29, 2021
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (ACOE) revert to pre-2015 regulatory program definition of “Waters of the United States.”

EPA Solicits Comments on PFAS Discharges in Five Point Source Categories
September 23, 2021
EPA solicits comments in five point source categories (PSCs) in the manufacture, use, treatment and discharge of PFAS.

PFAS Air Emissions Standards and Trends for Summer 2021
August 17, 2021
Environmental impacts of PFAS in ambient air leads to states implementing PFAS air-related thresholds.

Cryptocurrency: The Environmental Threats and Opportunities
August 9, 2021
Cryptocurrency (also known as crypto) is taking the fintech industry by storm, despite the economic experts who still dismiss it as a viable form of currency. Although often criticized for this volatility, whistleblowers are also further shining a light on the severe toll that these digital currencies are taking on the environment.

TRC Colorado PFAS Regulatory Update
July 21, 2021
Update on Colorado’s recent policies and plans to regulate new and historical discharges of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) into the environment.

2021 EPA TRI Reporting Requirements for Natural Gas Processing Facilities
July 12, 2021
Indication EPA finalizing a rule to add natural gas extraction or processing plants to EPCRA Toxics Release Inventory (TRI) reporting.

Implementing bioremediation at environmental cleanup sites: TRC experts weigh in at leading industry conference
May 17, 2021
TRC experts make several presentations at the Battelle conference about innovative approaches they have developed for implementing and monitoring bioremediation and the use of naturally-occurring or deliberately-introduced micro-organisms to break down environmental pollutants.

Interim Guidance on Destruction and Disposal of PFAS & Materials Containing PFAS
February 19, 2021
Interim Guidance from EPA identifies 6 materials that use or manufacture PFAS and approaches for disposal.

EPA continues to aggressively address PFAS wastewater with two new strategies
January 4, 2021
EPA takes steps toward PFAS wastewater and storm water permitting, and analytical methods for testing.

TRC Companies Inc. Acquires 1Source Safety and Health
November 11, 2020
TRC Companies (“TRC”), a leading technology-driven provider of end-to-end engineering, consulting and construction management solutions, has acquired 1Source Safety and Health, a firm that provides management consulting services in areas such as indoor air quality, asbestos management, industrial hygiene and safety management systems.

Ecological Risk of PFAS from AFFF-Impacted Sites
June 30, 2020
The facts on evaluating exposure to wildlife

TRC’s Reporting Tool Can Help Identify New PFAS under the TRI
May 19, 2020
While utilities often work in technical silos, NERC auditors are trained to cross check compliance evidence and data between interrelated standards.

EPA Issues Clarification of Free Product Removal Requirements
June 20, 2023
EPA recently clarified requirements for LNAPL recovery and remediation.

Microplastics ITRC Guidance Document and Training Available Soon!
February 23, 2023
Microplastic particles have been found in nearly every corner of the globe, but health effects and toxicity are only beginning to be understood. Because of their ubiquitous nature, microplastics present a challenge in both accurate sampling and source attribution. Microplastics are emerging as an environmental issue that regulators and industry will be increasingly focusing on in the coming years.

QA and Chemistry Services
February 23, 2023
TRC offers many QA and Chemistry services including data usability assessments, limited and full data validation reports, quality assurance project plan preparation, selection of appropriate analytical methodologies and laboratory audits.

Odor Evaluation Services
February 23, 2023
TRC is nationally recognized as an expert in the field of odor measurement, identification, modeling and control engineering. This presentation includes an overview of odor properties, odor evaluation, modeling and odor thresholds and outlines the four sensory properties: detectability, intensity, character and hedonic tone.

PFAS Fate and Transport
February 23, 2023
Understanding PFAS properties and behavior is key to effective detection and remediation.

PFAS Fate and Transport: Conceptual Site Models
February 23, 2023
The conceptual site model describes site-specific sources, release and transport mechanisms, exposure media, exposure points, exposure pathways and routes and potential human and/or ecological receptor populations.

EPA Announces $2 Billion in Funding to Address Emerging Contaminants in Drinking Water
February 14, 2023
Environmental Protection Agency Administrator Michael Regan announced $2 Billion in infrastructure funding to help the nation’s rural water supplies.

PFAS: Remedial Approaches
February 8, 2023
Remediating Per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from the soil and water requires effective techniques and innovative technologies. TRC’s experts are well versed in several remediation strategies intended to remove PFAS and prevent re-exposure.

Metals 101
February 8, 2023
Metals are naturally occurring elements in the Earth’s crust that enter the environment through natural processes. They can be found in groundwater, soil and sediment. The trophic transfer of these elements in aquatic and terrestrial food chains has important implications for wildlife and human health.

New National Emerging Contaminants Research Initiative
September 12, 2022
The Executive Office of the President of the United States announced a National Emerging Contaminant Research Initiative

The Best Process for Transforming Thermal Generation Power Plants
February 9, 2022
Faced with an aging fleet, stricter environmental regulations, reduced costs for natural gas and competition from renewables, more than 600 power plants have been decommissioned in the last 20 years, a pace that will increase with the announced closure of nearly 350 additional plants by 2025.

TRC Colorado PFAS Regulatory Update
July 21, 2021
Update on Colorado’s recent policies and plans to regulate new and historical discharges of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) into the environment.

Implementing bioremediation at environmental cleanup sites: TRC experts weigh in at leading industry conference
May 17, 2021
TRC experts make several presentations at the Battelle conference about innovative approaches they have developed for implementing and monitoring bioremediation and the use of naturally-occurring or deliberately-introduced micro-organisms to break down environmental pollutants.

Ecological Risk of PFAS from AFFF-Impacted Sites
June 30, 2020
The facts on evaluating exposure to wildlife

TRC Brings Environmental Services to Manchester with Second UK Office
March 5, 2020
In continuing to expand our presence in a key British market, TRC is opening our second UK office in Manchester, England

TRC Remediation Project at Roche Nutley Site in New Jersey Wins National Grand Prize for Sustainability
May 7, 2019
TRC was awarded the 2019 Grand Prize for Environmental Sustainability by the American Academy of Environmental Engineers & Scientists for the cleanup of the former Roche site in Nutley, N.J.

TRC Acquires Hazmat Assessment Firm American Environmental Consulting
January 3, 2018
TRC, a leader in engineering, environmental consulting and construction-management services, announced today that it has acquired American Environmental Consultants, Inc. of Weymouth, Mass., a hazardous materials assessment company.

EPA to Include CERCLA Sites and RCRA Facilities in Site Remediation NESHAP
June 23, 2016
EPA has published a proposed rule that would extend the requirements of the Site Remediation National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP) regulations to previously exempt soil and groundwater remediation activities under CERCLA and RCRA.

Successful Coal Ash Pond Management
July 10, 2014
Regulatory requirements, plant retirements, changes to facility operational profiles, environmental liability management and political and social pressures are among the factors driving utilities to close or consider closing their coal ash ponds.

Victoria Mann
Victor an Environmental Engineer and is TRC’s Technical Director for Water and Wastewater. Victor has 30 years of experience in remediation, water and wastewater treatment. Medina has a M.S. and Ph.D. in Civil/Environmental Engineering from the University of Southern California and is currently based in Jackson, Mississippi. Victor has five patents for innovative environmental technologies and specializes in developing effective solutions to challenging environmental problems. Contact Victor at vmedina@trccompanies.com.
Michael Eberle
Michael Eberle is a Technical Director within TRC in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Mr. Eberle is also a member of TRC’s Centers of Research & Expertise (CORE) for in‐situ remediation and treatment train optimization. Mr. Eberle has over 30 years of environmental consulting experience, including over 27 years of experience designing, troubleshooting, and managing the operation of multiphase hydrocarbon product extraction, bioventing, and in‐situ/ex-situ groundwater remediation systems. Additionally, Mr. Eberle is tasked with lending his chemistry background to understanding, characterizing, and tracking emerging chemicals under regulatory scrutiny.