Modernize Distribution Circuits
Improve Optimization. Learn more about the challenges, benefits and best practices for successfully implementing a modernization program on a large-scale distribution network.


In today’s dynamic power delivery world, utilities are increasingly focused on electrical distribution systems and reliability.
Distribution automation (DA) modernizes distribution circuits to enable automated operation, enhance real-time visibility of system events, and improve network optimization and reliability. This process involves implementing a system-wide distribution automation project, focusing on database management, equipment validation, and commissioning while addressing challenges related to project scale and duration.
In this webinar, hosted by T&D World, TRC and AVANGRID discuss their experiences with implementing a system wide distribution automation project. Topics covered include the concept of distribution automation, benefits of modernizing a distribution system, challenges of project scale and duration, database management, equipment validation and commissioning.
Improve Optimization. Learn more about the challenges, benefits and best practices for successfully implementing a modernization program on a large-scale distribution network.
Our practitioners share their insights and perspectives on the trends and challenges shaping the market.

Joint use has never been as important as it is today. With demand for telecommunications infrastructure skyrocketing, governments are investing big in initiatives like the $42.5 billion Broadband Equity Access Deployment Program (BEAD) and the $20.4 billion Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF).

NERC has submitted for FERC approval new compliance criteria for the registration of IBRs as part of continuing efforts to address reliability risks. It is critical for renewable energy developers, generation owners and transmission owners to understand the potential implications for interconnection studies and interconnection queues.

Avoid common pitfalls by following these five best practices

LOWELL, Mass. – TRC, a leading provider of end-to-end engineering, consulting and construction management solutions fueled by innovative technology, announced today it has acquired IJUS, a top power/utility engineering firm based in Gahanna, Ohio. Terms of the deal were not disclosed.

Discover how modern 3D facility mapping empowers utilities to modernize infrastructure, improve asset management, and enable remote workflows with accurate digital twins, delivering cost savings and operational efficiency.

In today’s changing energy landscape, grid resiliency is a top priority for all power system owners and operators. The ability to absorb disruptions and maintain power is crucial in an increasingly unpredictable world.

Implementing DERMS can come with challenges. By understanding the unique challenges related to DERMS and adopting the appropriate strategies to mitigate potential pitfalls, utilities can effectively integrate and coordinate DER deployment to align with regulatory commitments and broader business objectives.

In today’s rapidly evolving energy landscape, Independent System Operators (ISOs), Regional Transmission Organizations (RTOs) and utilities face unprecedented challenges in managing vast amounts of data.

LOWELL, Mass. – TRC, a leading provider of end-to-end engineering, consulting and construction management solutions fueled by innovative technology, announced today it has acquired IJUS, a top power/utility engineering firm based in Gahanna, Ohio. Terms of the deal were not disclosed. “By acquiring IJUS, TRC is now one of the leading power distribution engineering and consulting firms in the country,” said TRC CEO Chris Vincze. “This is a sector of the power market that is primed for strong growth over the next decade, with utilities looking to improve grid reliability and resiliency and harden their infrastructures. This move positions us to capitalize on that increased demand and continue to meet the growing needs of our clients.” Founded 13 years ago, IJUS has 320 employees across 15 offices in Ohio, California, Florida, Indiana, Missouri, North Carolina, Tennessee, West Virginia and Wisconsin. The firm specializes in tech-enabled engineering design, attachment services, field services and project management. “This is a great move for IJUS,” said Wil Schulze, company founder and president. “I am excited to bring the company into a premier organization like TRC, which will enable us to expand the breadth of our services and build on our client-first approach to doing business.” IJUS performs work for some of the nation’s largest utilities, including American Electric Power, Duke Energy, Wisconsin Public Service, Nashville Electric Service, Tampa Electric, and Dayton Power & Light. With the acquisition, TRC now has more than 700 employees delivering a full complement of transmission engineering and power distribution engineering in 30 states. “IJUS complements us geographically and helps expand the robust distribution engineering practice we already have,” said James Mayer, president of TRC’s Power Sector. “The company has a strong leadership team and is known throughout the industry for its creativity and innovation.” Since incorporating in January 2005, IJUS LLC has established itself as an industry leader in Engineering Design, Attachment Services, Field Services, Expanded Services, and Project Management for the Telecommunication and Electric Utility industries. We provide our clients with a wide range of skills and technical service knowledge deeply rooted in sound engineering principles. Every IJUS employee understands that our success hinges on our clients’ success. It’s a philosophy that drives our culture. Through collaboration and mutual achievements with our clients, IJUS is able to excel and form long-lasting partnerships.

NFPA 660 will make it easier for all industries to manage dust related hazards making for safer work environments.

On November 1, 2024, FERC Commissioners led a technical conference regarding co-locating large loads at generating facilities.

On Tuesday, December 17th, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) issued a final rule reclassifying several ozone nonattainment areas as “Serious” nonattainment for the 2015 ozone national ambient air quality standard.

In 2023, the Texas State Legislature approved Senate Bill 1397 and House Bill 1505, which require that “A person who holds a temporary permit or permit with an indefinite term shall report to the commission annually whether the activity subject to the permit is ongoing” and that the person “shall first report to the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality the status of the permitted activity not later than December 31, 2024”. The Texas Water Code has been amended to include this requirement in Sec. 5.587.

On November 1, 2024, FERC Commissioners led a technical conference regarding co-locating large loads at generating facilities.

Additional Restrictions for Major Modifications Other restrictions will come into play for new Major Sources, those that have a potential to emit 50 tons per year or more of VOC or NOx and “major modifications” that result in a VOC emission increase that exceeds 25 tons per year and also exceeds 25 tons per year when aggregated with all creditable increases and decreases in emissions of VOC from the source over any period of five consecutive years, which includes the calendar year in which the increase will occur. For sources that are major due to NOx emissions, a NOx emission increase that exceeds 25 tons per year and exceeds 25 tons per year when aggregated with creditable increases and decreases over the five-year period is also deemed to be a major modification. If a major modification occurs, the source is required to utilize the Lowest Achievable Emission Rate (or LAER) for the pollutant(s) that exceed 25 tons per year aggregated over the five-year period. However, Best Available Control Technology (BACT) can be substituted for LAER under certain conditions. Additionally, emissions must be offset as a means to advancing the area toward attaining the ozone standard. These same requirements will apply to newly constructed Major Sources. Upcoming Deadlines With these actions, the impacted areas will now have until August 3, 2027, to reach attainment. If they do not, USEPA is again obligated to reclassify ongoing nonattainment status to Severe nonattainment, reducing the Major Source threshold in half to just 25 tons per year. In the meantime, the states will be required to revise State Implementation Plans to demonstrate that attainment will be achieved by this deadline. A unique consideration in Wisconsin affects sources subject to a Registration Operation Permit. These permits establish annual emission limits as a percentage of the Major Source threshold (25, 50, or 80 percent depending on the Permit). For these sources, the annual emission limit for VOC and NOx will automatically be cut in half on January 16, 2025. Sources in the ozone nonattainment areas that hold these permits should evaluate whether the Registration Permit provides a long-term option given that the annual emission limits have been cut in half now and may again be cut in half in three years’ time. Next Steps: TRC Can Help TRC is available to support your air compliance and permitting needs by offering expert in-house resources to perform: Ambient Monitor Siting Evaluation Ambient Monitor Deployment, Operation and Maintenance For more information, contact Melanie Klamar, Robert VandenMeiracker and Mike Zebell.

This update provides details from FERC 2024 staff report from CIP audits, so utilities can improve compliance and reduce security risks.

Garanzuay Consulting provides a foundation in Ireland to continue TRC’s growth and expansion in Europe in support of the energy transition for all energy market participants.
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) recently released its 2024 State of Reliability report, examining power system performance in calendar year 2023.

Facility Ratings play a critical role in the reliable planning and operation of the Bulk Electric System (BES) and yet maintaining compliance with relevant NERC standards remains an industry challenge.
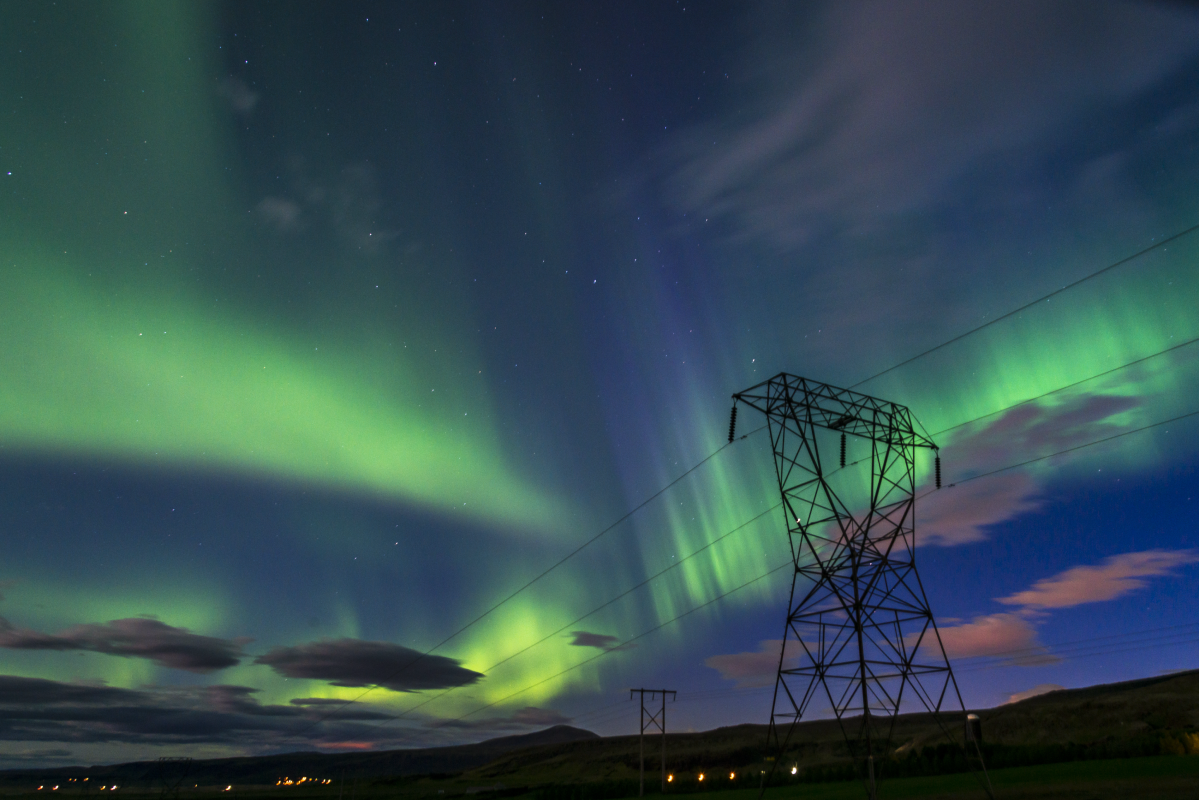

Learn about the recent geomagnetic disturbance which caused stakeholders within the bulk power system to react swiftly to protect grid reliability. Find out the impacts and what NERC and the industry are doing about it.

Joint use has never been as important as it is today. With demand for telecommunications infrastructure skyrocketing, governments are investing big in initiatives like the $42.5 billion Broadband Equity Access Deployment Program (BEAD) and the $20.4 billion Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF).

While utilities often work in technical silos, NERC auditors are trained to cross check compliance evidence and data between interrelated standards.

As part of NERC’s ongoing effort to bolster Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) requirements and enable the implementation of a security improvement concept known as virtualization.

In the actively changing energy landscape, utilities are grappling with many workforce-related challenges linked to the ongoing shift towards cleaner energy and the modernization of power grids. As veteran employees retire, it is critical to bridge the knowledge and skill gap by recruiting and developing younger talent.
Additional Restrictions for Major Modifications Other restrictions will come into play for new Major Sources, those that have a potential to emit 50 tons per year or more of VOC or NOx and “major modifications” that result in a VOC emission increase that exceeds 25 tons per year and also exceeds 25 tons per year when aggregated with all creditable increases and decreases in emissions of VOC from the source over any period of five consecutive years, which includes the calendar year in which the increase will occur. For sources that are major due to NOx emissions, a NOx emission increase that exceeds 25 tons per year and exceeds 25 tons per year when aggregated with creditable increases and decreases over the five-year period is also deemed to be a major modification. If a major modification occurs, the source is required to utilize the Lowest Achievable Emission Rate (or LAER) for the pollutant(s) that exceed 25 tons per year aggregated over the five-year period. However, Best Available Control Technology (BACT) can be substituted for LAER under certain conditions. Additionally, emissions must be offset as a means to advancing the area toward attaining the ozone standard. These same requirements will apply to newly constructed Major Sources. Upcoming Deadlines With these actions, the impacted areas will now have until August 3, 2027, to reach attainment. If they do not, USEPA is again obligated to reclassify ongoing nonattainment status to Severe nonattainment, reducing the Major Source threshold in half to just 25 tons per year. In the meantime, the states will be required to revise State Implementation Plans to demonstrate that attainment will be achieved by this deadline. A unique consideration in Wisconsin affects sources subject to a Registration Operation Permit. These permits establish annual emission limits as a percentage of the Major Source threshold (25, 50, or 80 percent depending on the Permit). For these sources, the annual emission limit for VOC and NOx will automatically be cut in half on January 16, 2025. Sources in the ozone nonattainment areas that hold these permits should evaluate whether the Registration Permit provides a long-term option given that the annual emission limits have been cut in half now and may again be cut in half in three years’ time. Next Steps: TRC Can Help TRC is available to support your air compliance and permitting needs by offering expert in-house resources to perform: Ambient Monitor Siting Evaluation Ambient Monitor Deployment, Operation and Maintenance For more information, contact Melanie Klamar, Robert VandenMeiracker and Mike Zebell.

NERC has submitted for FERC approval new compliance criteria for the registration of IBRs as part of continuing efforts to address reliability risks. It is critical for renewable energy developers, generation owners and transmission owners to understand the potential implications for interconnection studies and interconnection queues.

This blog delves into common misconceptions surrounding cloud migration in the utility industry, addressing concerns about security, reliability, regulatory compliance, cost effectiveness, and complexity, while highlighting the substantial benefits and strategies for successful adoption.

NERC has submitted proposed revisions to the EOP-012-2 – Extreme Cold Weather Preparedness and Operations standard, for FERC approval on an expedited basis. The proposed revisions address the remaining key recommendations from the FERC–NERC Joint Inquiry Report into Winter Storm Uri and directives arising from a 2023 FERC Order regarding the previously submitted cold weather standards.

Update to FAC-003-5 Brings Sweeping Changes to Transmission Classifications Starting April 1

Every NERC-registered utility must strive for continuous compliance with their portfolio of applicable NERC Reliability Standards

NERC has submitted its 2024-2026 Reliability Standards Development Plan to the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC), outlining its current priorities and future standard development plans to protect the reliability of the Bulk Power System over the next three years.

Inverter Based Resources are playing central role when it comes to adding new electric generation capacity into the bulk power system.

Locana, an international leader in spatial technology, received the Modern Network Management Award at the 2023 Esri Infrastructure Management and GIS (IMGIS) Conference held in Palm Springs, California, October 10-12, 2023.

Locana, an international leader in spatial technology, received Esri’s ArcGIS Cloud Services Specialty, which designates Locana as an expert in deploying and managing ArcGIS in cloud environments such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure.

As technology advances and cybersecurity threats loom, companies must prioritize communications retrofits and upgrades to ensure reliability, availability and business continuity.

Expert Discussions and Key Takeaways Focus on Physical Security

As the urgency to decarbonize and build resiliency grows, renewable energy continues to be a pivotal solution for reshaping the future of power in the U.S. From solar to wind, hydro, geothermal and biomass, each renewable resource has its sweet spot for efficient development, deployment and optimal performance. And while they all have their own pros and cons, it is imperative that we leverage them all into the energy mix to achieve decarbonization goals and ensure adequate capacity to meet increasing load demands.

As renewable energy proliferates across the US power system, the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) continues to actively address reliability risks resulting from the implementation of inverter-based resources (solar and wind generation technology) connected at both transmission and Distributed Energy Resources (DER) levels.

Leveraging new tools and technologies such as mixed and virtual reality (MR/VR) to develop a new generation of skilled engineers and technicians to maintain the reliability and resiliency of the future grid.

FERC issued a Final Rule directing NERC to develop a new or modified reliability standard addressing transmission system planning performance requirements for extreme heat or cold weather events.

The impact of adapting behavioral and cultural norms to focus on the principles of human performance cannot be underestimated in building the power workforce of the future.

According to the Edison Foundation’s Institute for Electric Innovation, over 124 million smart meters were expected to be installed in 78 percent of US households by the end of 2022.

EPA recently clarified requirements for LNAPL recovery and remediation.

The role of field service management continues to dominate the world economy, as the market grows at an exponential rate. The market was estimated at 3.2 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach 5.7 billion by the end of 2026.

On behalf of the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC), its President and CEO Jim Robb, recently presented to the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) a summary of NERC’s report on the effectiveness of NERC’s CIP-014 Physical Security Standard. There were almost 1,700 physical security incidents reported to the Electricity-Information Security Analysis Center (E-ISAC) in 2022, an increase of 10.5% from 2021.

As renewable energy development booms, and distributed energy resources (DERs) proliferate across the grid, the demand for a more efficient and timely interconnection process is at an all-time high. To meet regulatory deadlines and satisfy the needs of both developers and customers, utilities must tackle an increasingly complex array of system impact studies, analyses and reports, under ever shrinking timelines.

FERC directed NERC to develop Reliability Standards to implement INSM within trusted CIP environments.

TRC Companies announces its role as a consultant in supporting the new transmission project by LS Power Grid Maine.

NERC and TRE release the Odessa II Power System Disturbance Report

Additional Restrictions for Major Modifications Other restrictions will come into play for new Major Sources, those that have a potential to emit 50 tons per year or more of VOC or NOx and “major modifications” that result in a VOC emission increase that exceeds 25 tons per year and also exceeds 25 tons per year when aggregated with all creditable increases and decreases in emissions of VOC from the source over any period of five consecutive years, which includes the calendar year in which the increase will occur. For sources that are major due to NOx emissions, a NOx emission increase that exceeds 25 tons per year and exceeds 25 tons per year when aggregated with creditable increases and decreases over the five-year period is also deemed to be a major modification. If a major modification occurs, the source is required to utilize the Lowest Achievable Emission Rate (or LAER) for the pollutant(s) that exceed 25 tons per year aggregated over the five-year period. However, Best Available Control Technology (BACT) can be substituted for LAER under certain conditions. Additionally, emissions must be offset as a means to advancing the area toward attaining the ozone standard. These same requirements will apply to newly constructed Major Sources. Upcoming Deadlines With these actions, the impacted areas will now have until August 3, 2027, to reach attainment. If they do not, USEPA is again obligated to reclassify ongoing nonattainment status to Severe nonattainment, reducing the Major Source threshold in half to just 25 tons per year. In the meantime, the states will be required to revise State Implementation Plans to demonstrate that attainment will be achieved by this deadline. A unique consideration in Wisconsin affects sources subject to a Registration Operation Permit. These permits establish annual emission limits as a percentage of the Major Source threshold (25, 50, or 80 percent depending on the Permit). For these sources, the annual emission limit for VOC and NOx will automatically be cut in half on January 16, 2025. Sources in the ozone nonattainment areas that hold these permits should evaluate whether the Registration Permit provides a long-term option given that the annual emission limits have been cut in half now and may again be cut in half in three years’ time. Next Steps: TRC Can Help TRC is available to support your air compliance and permitting needs by offering expert in-house resources to perform: Ambient Monitor Siting Evaluation Ambient Monitor Deployment, Operation and Maintenance For more information, contact Melanie Klamar, Robert VandenMeiracker and Mike Zebell.

The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) recently proposed actions to keep the regulatory process and requirements ahead of reliability risks resulting from the accelerated deployment of Inverter Based Resources (IBR) based solar, wind and battery storage projects.

NERC report on best practices for utilities that have encountered facility ratings program challenges.

The rulemaking addresses improvements needed to reliably facilitate the power industry’s transition to renewable and distributed generating resources utilizing inverter-based technologies.

The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) recently released an Inverter-Based Resource (IBR) Strategy, which details the steps needed to successfully integrate IBR facilities into the planning and operation of the power system. The strategy was put in place due to the rapid interconnection of IBR systems, which are extensively used for solar and wind generating facilities, including new battery-based energy storage systems and are one of the most significant drivers of power grid transformation. Because of control system inconsistencies, IBR facilities pose well-documented risks to power system reliability when this strategy’s practices are not adhered to. NERC’s plan calls attention to the need for thoughtful integration of IBRs and identifies current and future work required to mitigate reliability risks resulting from the deployment of this technology.

The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) recently released its 2022 State of Reliability report, which examines power system performance in calendar year 2021 and evaluates reliability performance trends. The 2022 report identified six key findings regarding power system performance that are summarized as follows:

NERC has proposed implementation guidance for PRC-019-2, the standard that verifies coordination of generating unit facility or synchronous condenser voltage regulating controls, limit functions, equipment capabilities and protection system settings.

Reliability Standards FAC-001-4 and FAC-002-will resolve uncertainty regarding the meaning of “materially modify” under the currently effective standards.

Updated Order will have significant impact on NERC compliance programs related to both PRC standards and facilities ratings. Utilities should review the Order’s requirements and prepare for changes needed to remain compliant.

Locana, a global leader in technology consulting and geospatial systems development, today announced the successful deployment of its LemurSM Solution by Omaha Metropolitan Utilities District (M.U.D.).

Changes to PRC-024-3 in support of inverter-based generation performance are going into effect in October of this year. Interconnection programs and documentation procedures may need to be updated in order to maintain compliance.

There are significant technical challenges involved in implementing Dynamic Line Ratings in the planning and operation of utility systems. Utilities should be prepared to modify their NERC compliance programs as necessary to address the potential introduction of DLR in their businesses.

Modernizing utility equipment, standards and processes pays dividends for improved safety, security and reliability. But transitioning to a new high-tech system model can be challenging.

NERC has issued a new report highlighting the key attributes of various inverter controls to support proper implementation and to protect reliability.

In a recently released reliability guideline, NERC recommends additional approaches for Underfrequency Load Shedding (UFLS) program design to help utilities effectively consider the effects of Distributed Energy Resources (DERs). The guidance was developed to address the accelerated transition of the power system to locally installed, decarbonized resources that depend on inverters. These new technologies introduce operational controls issues into the electric grid. UFLS data gathering and analysis methodologies may require modification to address reliability risks.

Between 18 and 36 percent of reported utility misoperations were attributed to issues that could have been detected through a properly implemented PSC.

The in-depth report outlines twenty-eight recommendations to address freeze reliability failures, including operating practices and recommendations for NERC standards modifications surrounding generator winterization and gas-electric coordination.

At its November 2021 meeting, NERC’s Board of Trustees took aggressive action to advance critical cold weather Reliability Standards. Most notably, the group approved the 2022-2024 Reliability Standards Development Plan, which prioritizes standards projects for the coming years including a resolution to include new cold weather operations, preparedness and coordination standards as high priority development projects.

With a focus on the reliability impact of extreme weather and the shortcomings of current system planning approaches, both NERC and FERC conference participants opened the door to potential forthcoming compliance standard enhancements or changes.

While NERC has analyzed multiple similar events in California, this is the first disturbance involving a widespread reduction of PV resource power output observed in the Texas Interconnection.

Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E) formally announced TRC as the designated lead Program Implementer for the Statewide New Construction (SWNC) Residential All-Electric and Mixed Fuel Programs following a competitive solicitation process.
Snohomish PUD selected TRC to implement, integrate and deliver their meter data management system (MDMS) on the Siemens EnergyIP® platform as a part of the utility’s Connect Up program.

The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission has approved changes to three mandatory NERC Reliability Standards that aim to better prepare the North American power system to withstand extreme cold weather events.

ERCOT’s recently released “Roadmap to Improving Grid Reliability” presents a plan for change in Texas that includes increasing electric power generation and purchasing significantly more power reserves.

With 2020 right around the corner, there are many new NERC standards and standards requirements set to go into effect in the areas of Critical Infrastructure Protection and Transmission Operations and Planning.

As part of its grid enhancement program, OG&E will leverage collaborative AI-powered image recognition technology that enables engineers to complete distribution pole inspections with greater accuracy and helps to reduce manual review of images.

Opposites attract, and information technology (IT) and operational technology (OT) are no exception. At one end of the digital grid sits IT as a business application, while OT exists at the other end of the digital grid as an asset-oriented application. For decades, IT and OT have been operating separately and are often physically isolated.

A successful IT/OT convergence strategy involves identifying desired outcomes, managing the fragmentation of OT solutions, and developing common key performance indicators (KPIs) for both IT and OT teams. This approach helps in optimizing resources, driving effective collaboration, and ensuring a smooth transition towards a unified IT/OT environment.

Two recent actions will change the current system planning, investment needs and operating procedures for electric utilities. New infrastructure investments and more robust compliance programs will be needed.

Today, TRC announced the expansion of its digital capabilities with the acquisition of Quatric, a Montreal, QC and Quincy, MA-based firm that provides engineering services and technology solutions to electric and gas utilities.

FAC-008 is one of the most data-intensive standards in the NERC regulatory framework. Compliance has been difficult for many utilities. Recently, FERC made public it’s intent to address serious allegations of facility ratings violations, including a lack of rigor by one utility.

In preparing for Utility Network Migration, taking an intermediate approach will allow you to resolve some key points. Utility Network Migration will run smoother if you build a “sandbox environment” and begin to 1) prioritize features 2) explore licensing options and 3) practice moving data.

While ArcGIS on HANA implementation patterns are emerging rapidly, we continue to hear 5 persistent questions about how implementing ArcGIS on HANA would benefit an organization. Let’s walk through these 5 questions, I’ll show you how we help you get started with ArcGIS on HANA. Then you may realize the benefits this solution promises.

NERC’s CIP-008 standard aims to mitigate reliability risks resulting from a Cyber Security Incident by specifying incident response requirements. Newly proposed revisions would augment mandatory reporting to include incidents that compromise, or attempt to compromise, a utility’s Electronic Security Perimeter (ESP) or associated Electronic Access Control or Monitoring Systems (EACMS).

The latest weather impacts to power reliability have accelerated the need for mandatory regulatory compliance changes.

Today TRC Companies (“TRC”), announces the expansion of its advanced energy capabilities with the acquisition of EMI Consulting (“EMI”), a Seattle based firm that consults on the strategic development of clean energy solutions including energy efficiency, demand management, decarbonization and customer engagement.

In its 2020 Report on CIP Reliability Audits, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission found that most of the cybersecurity protection processes and procedures adopted by utilities met the mandatory CIP requirements for protecting the Bulk Electric System. However, there are areas for improvement.

Dominion Energy, one of the nation’s largest producers and transporters of energy, has partnered with TRC Digital to evaluate, implement and integrate technology to further the utility’s distributed energy goals. TRC Digital will facilitate Dominion Energy’s strategy development and technology execution, allowing Dominion Energy and its customers to accelerate the shift to distributed energy resources (DER) and net carbon reduction.

The Report identifies areas of ongoing concern including generation reserve margins and the reliability risk from shifting the resource mix toward renewables.

Together, TRC and Reactive combine TRC’s industry-leading power engineering expertise with Reactive’s machine learning software to provide utility teams with high-resolution frequency monitoring and automatic event analysis.

On July 10, 2020 NERC released new Lessons Learned guidance to address situations where multiple composite protection systems have misoperated as a result of mixing protective relay technologies at the remote terminals of directional comparison blocking (DCB) schemes. This technical information will help utilities improve the reliability of the Bulk Power System.

On July 9, 2020 NERC standard PRC-024-3 was approved, paving the way for improved protection systems in support of keeping generating resources connected during defined frequency and voltage excursions.

FERC has released a notice of inquiry seeking comments on potential enhancements to NERC’s Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) Reliability Standards.

As part of TRC’s LineHub solution, Treverity helps transmission engineers get a holistic view of the grid through powerful digital data visualization and a customer-centric user interface.

As we look to spur strategic electrification across the US, it will be up energy providers and solution implementers to continue sharing ideas, insights and lessons learned

NERC’s 2019 ERO Reliability Risk Priorities Report identified and prioritized the major risks facing the utility industry with a particular focus on security issues.

LOWELL, Mass. – TRC, a leading provider of end-to-end engineering, consulting and construction management solutions fueled by innovative technology, announced today it has acquired IJUS, a top power/utility engineering firm based in Gahanna, Ohio. Terms of the deal were not disclosed.

This month, NERC released the first draft of its 2019 Compliance Monitoring and Enforcement Plan (CMEP) which identifies power delivery system risks and outlines compliance audit requirements for next year. The risk elements outlined in the plan include significant differences from previous years, as shown in the table below. Each NERC region must consider these risks as they develop their monitoring and audit scopes for utilities. Utilities should be prepared to be audited and implement any necessary compliance initiatives in these areas.

The approval of NERC Standard PRC-005-2 extends protection system maintenance obligations to Generators and crates one comprehensive standard establishing minimum maintenance activities and maximum time intervals for protection systems and load shedding equipment affecting the bulk electric system.

NERC has proposed implementation guidance for PRC-019-2, the standard that verifies coordination of generating unit facility or synchronous condenser voltage regulating controls, limit functions, equipment capabilities and protection system settings.

Reliability Standards FAC-001-4 and FAC-002-will resolve uncertainty regarding the meaning of “materially modify” under the currently effective standards.

Updated Order will have significant impact on NERC compliance programs related to both PRC standards and facilities ratings. Utilities should review the Order’s requirements and prepare for changes needed to remain compliant.

Changes to PRC-024-3 in support of inverter-based generation performance are going into effect in October of this year. Interconnection programs and documentation procedures may need to be updated in order to maintain compliance.

There are significant technical challenges involved in implementing Dynamic Line Ratings in the planning and operation of utility systems. Utilities should be prepared to modify their NERC compliance programs as necessary to address the potential introduction of DLR in their businesses.

NERC has issued a new report highlighting the key attributes of various inverter controls to support proper implementation and to protect reliability.

In a recently released reliability guideline, NERC recommends additional approaches for Underfrequency Load Shedding (UFLS) program design to help utilities effectively consider the effects of Distributed Energy Resources (DERs). The guidance was developed to address the accelerated transition of the power system to locally installed, decarbonized resources that depend on inverters. These new technologies introduce operational controls issues into the electric grid. UFLS data gathering and analysis methodologies may require modification to address reliability risks.

With 2020 right around the corner, there are many new NERC standards and standards requirements set to go into effect in the areas of Critical Infrastructure Protection and Transmission Operations and Planning.

The Report identifies areas of ongoing concern including generation reserve margins and the reliability risk from shifting the resource mix toward renewables.

On July 10, 2020 NERC released new Lessons Learned guidance to address situations where multiple composite protection systems have misoperated as a result of mixing protective relay technologies at the remote terminals of directional comparison blocking (DCB) schemes. This technical information will help utilities improve the reliability of the Bulk Power System.

On July 9, 2020 NERC standard PRC-024-3 was approved, paving the way for improved protection systems in support of keeping generating resources connected during defined frequency and voltage excursions.

NERC’s PRC-027-1 standard was approved by FERC in 2018 and is set to go into effect on October 1, 2020. Utilities should begin preparing now to meet compliance requirements which include significant system studies.

Looking ahead to the many changes coming to North America’s Bulk Power System (BPS), NERC’s 2019 ERO Reliability Risk Priorities Report highlights the top issues requiring industry and regulatory attention and recommends actions for the ongoing protection of BPS reliability.

Renewable energy systems have dramatically changed the power generation resource mix. These new generation technologies no longer involve directly coupled rotating generators which were once standard in the industry. Now, inverters that change Direct Current (DC) electricity to the Alternating Current (AC) electricity suitable for delivery via AC transmission systems are becoming more prevalent, raising reliability…

LOWELL, Mass. – TRC, a leading provider of end-to-end engineering, consulting and construction management solutions fueled by innovative technology, announced today it has acquired IJUS, a top power/utility engineering firm based in Gahanna, Ohio. Terms of the deal were not disclosed. “By acquiring IJUS, TRC is now one of the leading power distribution engineering and consulting firms in the country,” said TRC CEO Chris Vincze. “This is a sector of the power market that is primed for strong growth over the next decade, with utilities looking to improve grid reliability and resiliency and harden their infrastructures. This move positions us to capitalize on that increased demand and continue to meet the growing needs of our clients.” Founded 13 years ago, IJUS has 320 employees across 15 offices in Ohio, California, Florida, Indiana, Missouri, North Carolina, Tennessee, West Virginia and Wisconsin. The firm specializes in tech-enabled engineering design, attachment services, field services and project management. “This is a great move for IJUS,” said Wil Schulze, company founder and president. “I am excited to bring the company into a premier organization like TRC, which will enable us to expand the breadth of our services and build on our client-first approach to doing business.” IJUS performs work for some of the nation’s largest utilities, including American Electric Power, Duke Energy, Wisconsin Public Service, Nashville Electric Service, Tampa Electric, and Dayton Power & Light. With the acquisition, TRC now has more than 700 employees delivering a full complement of transmission engineering and power distribution engineering in 30 states. “IJUS complements us geographically and helps expand the robust distribution engineering practice we already have,” said James Mayer, president of TRC’s Power Sector. “The company has a strong leadership team and is known throughout the industry for its creativity and innovation.” Since incorporating in January 2005, IJUS LLC has established itself as an industry leader in Engineering Design, Attachment Services, Field Services, Expanded Services, and Project Management for the Telecommunication and Electric Utility industries. We provide our clients with a wide range of skills and technical service knowledge deeply rooted in sound engineering principles. Every IJUS employee understands that our success hinges on our clients’ success. It’s a philosophy that drives our culture. Through collaboration and mutual achievements with our clients, IJUS is able to excel and form long-lasting partnerships.
"*" indicates required fields