Author: Dwayne Stradford | May 6, 2024
In 2003, the Northeastern United States and parts of Canada experienced a significant and disruptive blackout event with root causes related to trees (right of way vegetation management), training (system control center personnel), tools (real-time situational awareness) and wide-area support (inadequate reliability coordinator diagnostics). In the decade since, NERC has developed a host of new, interrelated mandatory compliance standards to address reliability shortcomings and encourage the power industry to improve overall collaboration and work processes to ensure uninterrupted access to electricity for all.
The proliferation of interrelated NERC standards has encouraged a spirit of communication, collaboration and cooperation across internal utility departments, requiring a corporate community approach that emphasizes a culture of teamwork and safety for ultimate compliance success.
Interrelationships Between NERC Standards
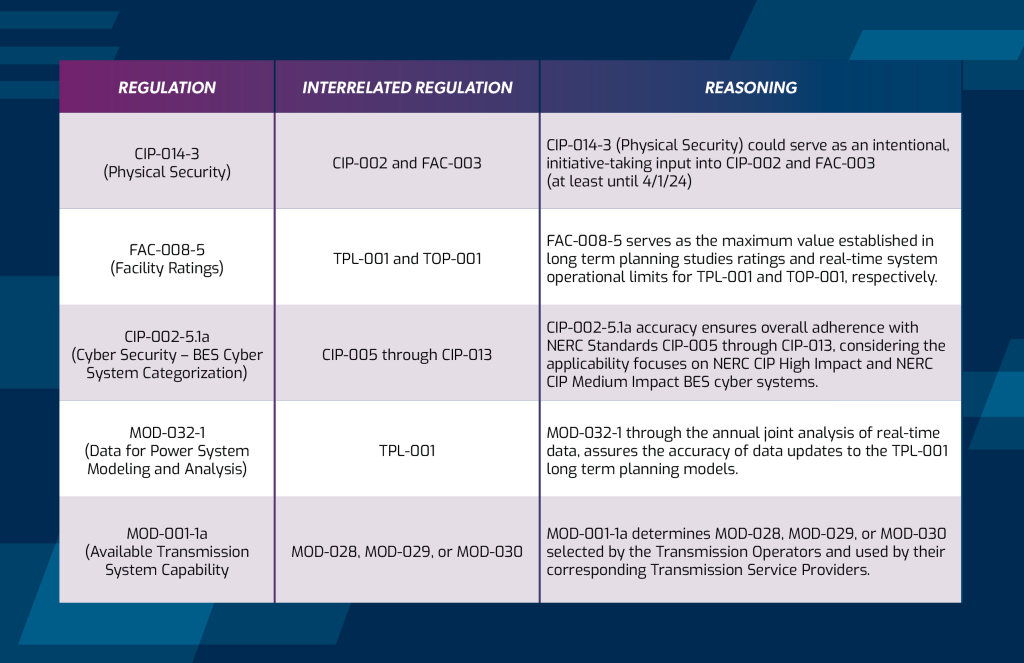
A good portion of NERC Standards (and corresponding standard requirements) are interrelated either directly or indirectly. There are standard requirement outputs that serve as inputs into other standard requirements or depend on deliverables from them. Examples of compliance tie-ins are pictured.
When drafting your operating policies, along with NERC Audit Readiness documentation (like RSAWs), compliance stakeholders should contemplate these internal links when preparing for any future Regional Entity (RE) engagements. This would be an optimal time to formally integrate the objective QA/QC document reviews from the leaders in the other impacted departments. It clearly demonstrates to auditors that there is an intentional effort to breakdown operational silos and encourage compliance awareness across corporate boundaries. Furthermore, the better that individual contributors understand the importance of their work output within the broader context of overall NERC compliance, the more likely that they are to become more focused on the quality of their work.
Positive Outcomes That Follow NERC Compliance Awareness
There are many positive outcomes when stakeholders have an improved sense of their NERC compliance awareness, including:
- Mitigating repeat violations and unforced compliance errors. This creates an overall greater culture of compliance through this community effort and helps to improve an entity’s NERC compliance reputation with their Regulators.
- Increasing overall corporate productivity. With a decline in incident management activities and continuously implementing mitigation plans, individual contributors and subject matter experts can spend more time on executing core company duties and responsibilities.
- Avoiding financial penalties. There is a direct, positive impact on shareholder value, since NERC fines and penalties are not recoverable.
Increasing Compliance Awareness and Promoting Best Practices
Your company’s compliance success is influenced by how willing all compliance stakeholders are and how aware they are that their work is externally influenced, in conjunction with how their work affects other corporate compliance colleagues. Action items for companies to consider implementing to improve their overall compliance awareness and performance include:
- Schedule ongoing, periodic coordination discussions that help open lines of communication between all mutually impacted compliance stakeholders.
- Establish a centralized, corporate source of truth to breakdown compliance silos.
- Perform annual QA/QC document reviews of all policies, procedures and guidelines with NERC compliance implications. This includes incorporating policy reviewers, signatures and approvers from other accountable organizations.
- Cultivate, Acknowledge and Submit NERC compliance evidence throughout the audit cycle, as opposed to 30 to 90 days prior to a formal audit. This requires stakeholders to compile NERC compliance evidence periodically, such as monthly or quarterly (cultivate), self-certify evidence throughout the audit cycle (acknowledge), and locally archive certified NERC evidence in parallel with transmittal to the Regions (submit).
- Encourage the proactive compliance engagement from ancillary stakeholders that do not have any official NERC Registered Function. For example, Corporate Telecommunications with supporting COM-001-3 (Communications), or Corporate Human Resources with supporting CIP-004-7 (Cyber Security – Personnel & Training). Notably, this tends to require executive leadership motivation to inspire active employee participation.
- Ongoing, continuous training and awareness seminars to keep NERC Compliance at the forefront of everybody’s focus. Use near misses and close calls as the background for future training materials and highlight ongoing required training explicitly called out in the NERC standards.

Next Steps
It is essential that adherence with NERC compliance obligations is considered by all stakeholders from a wider corporate perspective, as opposed to a parochial team by team focus. The work inside the office, as well as the efforts out in the field, have some direct or indirect correlation to your company’s overall compliance posture. It is imperative to gain a better understanding of the work that you are responsible for executing and how it impacts the other compliance stakeholders, within your individual boundary of influence. It is important to remember these key compliance takeaways when considering a corporate community approach:
- NERC Compliance is a team sport. No one individual or department is an island onto themselves.
- The Regional Entities (RE) audit (e.g. Reliability First, Midwest Reliability Organization, etc.) assess your company’s overall compliance adherence as a whole enterprise. You are not being audited or graded on a department-by-department basis.
- It is essential to demonstrate the principles of collaboration, cooperation and transparency while in front of the auditors. Once it is clear that your company is not internally aligned amongst themselves, the line of questioning will help further explore any lack of transparency and communication amongst the various compliance stakeholders.

TRC Can Help
At TRC, we focus on enhancing shareholder value and corporate compliance reputation by mitigating the risk of non-recoverable NERC fines, improving audit readiness, eliminating silos, enhancing operational efficiency, streamlining workflows and establishing a centralized document repository for core compliance data.
Our tested practitioners have decades of experience with utility-based regulatory requirements. We conduct NERC gap assessments, execute audit readiness initiatives and power flow studies. We also support physical and cyber security assessments and onsite walk downs of transmission lines and substations to verify FAC-008 facility rating data values. Our team is accustomed to working closely with utilities to analyze, evaluate and prepare for cold and extreme weather events, PRC related relay studies and MOD related studies.
Sharing Our Perspectives
Our practitioners share their insights and perspectives on the trends and challenges shaping the market.

Enhance Security Planning and Reporting with Key Takeaways from NERC’s 2024 Cyber Report
May 30, 2025
NERC has issued its 2024 Cyber Security Report, reviewing reported incidents related to Reliability Standard CIP-008-6.

Challenges Surround Approval of PRC-029-1
April 30, 2025
Approved by the Board of Trustees in 2024, NERC’s PRC-029-1 standard sets inverter-based resources (IBR) performance requirements ensuring they can “withstand voltage or frequency disturbances inside defined limits” and can “continue operating as specified.”

FERC Examines Co-Located Load and Generation Rule
April 21, 2025
Since FERC hosted its technical conference in late 2024, many industry stakeholders have submitted their comments addressing how to study and potentially regulate new co-located load and generation.

Cybersecurity Threats Lead NERC to Modify CIP Standards
March 11, 2025
Cybersecurity threats to the Bulk Electric System (BES) are escalating, with attackers continuously evolving their tactics to target critical infrastructure.

Large Data Center Load Loss Calls for System Impact Studies
March 3, 2025
On January 8, 2025, NERC released its review of an incident where the sudden loss of approximately 1,500 MW of data center load in Virginia exposed major reliability vulnerabilities in the Bulk Electric System (BES). This unanticipated event triggered voltage spikes and frequency imbalances, highlighting the need for system planners and operators to anticipate and mitigate these risks nationwide

NERC Approves New Extreme Weather Planning Standard
January 22, 2025
On December 10, 2024, NERC’s Board of Trustees approved standard TPL-008-1 Transmission System Planning Performance Requirements for Extreme Temperature Events. The petition to approve the TPL-008-1 standard was filed with the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) on December 17, 2024 and will initiate the implementation plan upon final approval.

FERC Issues Guidance to Improve Power System Security and CIP Compliance
September 30, 2024
This update provides details from FERC 2024 staff report from CIP audits, so utilities can improve compliance and reduce security risks.
NERC Releases 2024 State of Reliability Report
September 19, 2024
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) recently released its 2024 State of Reliability report, examining power system performance in calendar year 2023.

Facility Ratings Compliance Through a Corporate Community Approach
August 30, 2024
Facility Ratings play a critical role in the reliable planning and operation of the Bulk Electric System (BES) and yet maintaining compliance with relevant NERC standards remains an industry challenge.

Extreme Geomagnetic Disturbances Impact NERC Planning
August 8, 2024
Learn about the recent geomagnetic disturbance which caused stakeholders within the bulk power system to react swiftly to protect grid reliability. Find out the impacts and what NERC and the industry are doing about it.

Consistent NERC Compliance Evidence for Successful Audit Outcomes
June 27, 2024
While utilities often work in technical silos, NERC auditors are trained to cross check compliance evidence and data between interrelated standards.

New NERC Standards Help Protect Against Cyber Attacks
May 23, 2024
As part of NERC’s ongoing effort to bolster Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) requirements and enable the implementation of a security improvement concept known as virtualization.

NERC Proposes Changes to Registration Criteria for Inverter Based Resources (IBRs)
April 19, 2024
NERC has submitted for FERC approval new compliance criteria for the registration of IBRs as part of continuing efforts to address reliability risks. It is critical for renewable energy developers, generation owners and transmission owners to understand the potential implications for interconnection studies and interconnection queues.

NERC Proposes Clarifications to EOP Cold Weather Standards
March 26, 2024
NERC has submitted proposed revisions to the EOP-012-2 – Extreme Cold Weather Preparedness and Operations standard, for FERC approval on an expedited basis. The proposed revisions address the remaining key recommendations from the FERC–NERC Joint Inquiry Report into Winter Storm Uri and directives arising from a 2023 FERC Order regarding the previously submitted cold weather standards.

Update to FAC-003-5 Brings Sweeping Changes to Transmission Classifications Starting April 1
March 19, 2024
Update to FAC-003-5 Brings Sweeping Changes to Transmission Classifications Starting April 1

Prevent NERC Compliance Failures with Readiness Reviews
February 20, 2024
Every NERC-registered utility must strive for continuous compliance with their portfolio of applicable NERC Reliability Standards

NERC Releases 2024-2026 Standards Development Plan
January 26, 2024
NERC has submitted its 2024-2026 Reliability Standards Development Plan to the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC), outlining its current priorities and future standard development plans to protect the reliability of the Bulk Power System over the next three years.

NERC & FERC Release Winter Storm Elliott Report
January 2, 2024
NERC and FERC have released their final report on Winter Storm Elliott which provides reinforcement for recommendations in prior cold weather-related disturbance event reports. The Report identifies critical reliability performance shortcomings and the reliability related near misses. NERC states that a crisis was “narrowly dodged.” The Report outlines the steps the industry must take to avoid a repeat in the future.

FERC Order 901 Calls for Standards to Address IBR Reliability Gaps
November 27, 2023
Inverter Based Resources are playing central role when it comes to adding new electric generation capacity into the bulk power system.

NERC Releases Inverter Based Resources Webinar Series
October 19, 2023
As the power delivery system continues to rapidly evolve due to decarbonization policy initiatives, inverter-based resources (IBRs) are playing an ever-more significant role in generation additions to the bulk power system. NERC and other technical organizations have taken numerous actions to support the reliable integration of these resources.

FERC Issues Order 2023 to Resolve Interconnection Process Issues
September 25, 2023
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission has approved Order 2023 to facilitate and improve the speed and reliability of adding new energy resources to the power system

CFATS Program Expires but Reauthorization Anticipated this Fall
September 6, 2023
Regulated organizations should continue to follow DHS cybersecurity requirements.

FERC Hosts Technical Conference on the Effectiveness and Improvements to CIP-014-3
August 30, 2023
Expert Discussions and Key Takeaways Focus on Physical Security

Intro to NERC Regulatory Guidance on Inverter-Based Resources
August 29, 2023
As renewable energy proliferates across the US power system, the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) continues to actively address reliability risks resulting from the implementation of inverter-based resources (solar and wind generation technology) connected at both transmission and Distributed Energy Resources (DER) levels.

FERC Extreme Weather Initiative Will Change the Transmission Planning Process
July 26, 2023
FERC issued a Final Rule directing NERC to develop a new or modified reliability standard addressing transmission system planning performance requirements for extreme heat or cold weather events.

FERC Approves Plan to Register Certain Inverter-Based Resources as part of NERC Mandatory Standards Compliance Program
June 21, 2023
FERC issued an order approving NERC’s compliance filings.

NERC Files Report on Effectiveness on CIP-014 Physical Security Standard
May 25, 2023
On behalf of the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC), its President and CEO Jim Robb, recently presented to the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) a summary of NERC’s report on the effectiveness of NERC’s CIP-014 Physical Security Standard. There were almost 1,700 physical security incidents reported to the Electricity-Information Security Analysis Center (E-ISAC) in 2022, an increase of 10.5% from 2021.

FERC Issues Order on Cold Weather Reliability Standards
April 27, 2023
FERC has approved two NERC proposed cold weather-related reliability standards.

FERC Orders Internal Network Security Monitoring Rule to be Finalized
March 14, 2023
FERC directed NERC to develop Reliability Standards to implement INSM within trusted CIP environments.

Insights from the Odessa II Power System Disturbance
February 22, 2023
NERC and TRE release the Odessa II Power System Disturbance Report

New FERC Orders Will Change Regulatory Process for Inverter Based Resources
January 9, 2023
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) recently proposed actions to keep the regulatory process and requirements ahead of reliability risks resulting from the accelerated deployment of Inverter Based Resources (IBR) based solar, wind and battery storage projects.

NERC Releases Facilities Ratings Best Practices Report
December 19, 2022
NERC report on best practices for utilities that have encountered facility ratings program challenges.

NERC Files Comments in the FERC Generator Interconnection Notice of Proposed Rulemaking
November 21, 2022
The rulemaking addresses improvements needed to reliably facilitate the power industry’s transition to renewable and distributed generating resources utilizing inverter-based technologies.

NERC Releases Inverter-Based Resource Strategy Plan
October 25, 2022
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) recently released an Inverter-Based Resource (IBR) Strategy, which details the steps needed to successfully integrate IBR facilities into the planning and operation of the power system. The strategy was put in place due to the rapid interconnection of IBR systems, which are extensively used for solar and wind generating facilities, including new battery-based energy storage systems and are one of the most significant drivers of power grid transformation. Because of control system inconsistencies, IBR facilities pose well-documented risks to power system reliability when this strategy’s practices are not adhered to. NERC’s plan calls attention to the need for thoughtful integration of IBRs and identifies current and future work required to mitigate reliability risks resulting from the deployment of this technology.

NERC Releases 2022 State of Reliability Report
September 16, 2022
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) recently released its 2022 State of Reliability report, which examines power system performance in calendar year 2021 and evaluates reliability performance trends. The 2022 report identified six key findings regarding power system performance that are summarized as follows:

NERC Proposes Implementation Guidance for PRC-019-2
August 22, 2022
NERC has proposed implementation guidance for PRC-019-2, the standard that verifies coordination of generating unit facility or synchronous condenser voltage regulating controls, limit functions, equipment capabilities and protection system settings.

Revisions to FAC-001 and FAC-002 Submitted for FERC Approval
July 12, 2022
Reliability Standards FAC-001-4 and FAC-002-will resolve uncertainty regarding the meaning of “materially modify” under the currently effective standards.

FERC Order No. 881-A Has Implications for NERC Compliance Programs
June 23, 2022
Updated Order will have significant impact on NERC compliance programs related to both PRC standards and facilities ratings. Utilities should review the Order’s requirements and prepare for changes needed to remain compliant.

NERC’s Revised PRC-024-3 Standard for Inverter-Based Generation Effective in October 2022
May 11, 2022
Changes to PRC-024-3 in support of inverter-based generation performance are going into effect in October of this year. Interconnection programs and documentation procedures may need to be updated in order to maintain compliance.

FERC Issues Notice of Inquiry Regarding Dynamic Line Ratings
April 25, 2022
There are significant technical challenges involved in implementing Dynamic Line Ratings in the planning and operation of utility systems. Utilities should be prepared to modify their NERC compliance programs as necessary to address the potential introduction of DLR in their businesses.

New NERC Guidance Supports the Implementation of Grid Forming Inverters
March 8, 2022
NERC has issued a new report highlighting the key attributes of various inverter controls to support proper implementation and to protect reliability.

NERC Recommends Approaches for Underfrequency Load Shedding Programs
February 24, 2022
In a recently released reliability guideline, NERC recommends additional approaches for Underfrequency Load Shedding (UFLS) program design to help utilities effectively consider the effects of Distributed Energy Resources (DERs). The guidance was developed to address the accelerated transition of the power system to locally installed, decarbonized resources that depend on inverters. These new technologies introduce operational controls issues into the electric grid. UFLS data gathering and analysis methodologies may require modification to address reliability risks.

NERC and FERC Recommend Protection System Commissioning Improvements
January 18, 2022
Between 18 and 36 percent of reported utility misoperations were attributed to issues that could have been detected through a properly implemented PSC.

FERC & NERC Issue Joint Report on Freeze Reliability Failures
December 15, 2021
The in-depth report outlines twenty-eight recommendations to address freeze reliability failures, including operating practices and recommendations for NERC standards modifications surrounding generator winterization and gas-electric coordination.

NERC Accelerates Additional Cold Weather Standards Changes
November 22, 2021
At its November 2021 meeting, NERC’s Board of Trustees took aggressive action to advance critical cold weather Reliability Standards. Most notably, the group approved the 2022-2024 Reliability Standards Development Plan, which prioritizes standards projects for the coming years including a resolution to include new cold weather operations, preparedness and coordination standards as high priority development projects.

PRC-002-2 Disturbance Monitoring and Reporting Standard: Initial Mandatory Implementation Plan Dates Approach
November 18, 2021
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission approved PRC-002-2 in September, 2015. The initial due date for system studies necessary to identify locations for the collection of disturbance related data under Requirement R1 is January 1, 2017.

New Potential Compliance Standards Identified at FERC Technical Conference on Reliability
October 18, 2021
With a focus on the reliability impact of extreme weather and the shortcomings of current system planning approaches, both NERC and FERC conference participants opened the door to potential forthcoming compliance standard enhancements or changes.

NERC Issues Odessa Texas Disturbance Report
September 29, 2021
While NERC has analyzed multiple similar events in California, this is the first disturbance involving a widespread reduction of PV resource power output observed in the Texas Interconnection.

FERC Approves Modifications to NERC’s Cold Weather-Related Standards
September 7, 2021
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission has approved changes to three mandatory NERC Reliability Standards that aim to better prepare the North American power system to withstand extreme cold weather events.



Electric Reliability Council of Texas Releases 60-Point Plan for Change
August 23, 2021
ERCOT’s recently released “Roadmap to Improving Grid Reliability” presents a plan for change in Texas that includes increasing electric power generation and purchasing significantly more power reserves.

Prepare for Upcoming NERC Compliance Deadlines
August 20, 2021
With 2020 right around the corner, there are many new NERC standards and standards requirements set to go into effect in the areas of Critical Infrastructure Protection and Transmission Operations and Planning.

Developments in Texas and Nationally Mandate Extreme Weather Responses to Protect Reliability
July 23, 2021
Two recent actions will change the current system planning, investment needs and operating procedures for electric utilities. New infrastructure investments and more robust compliance programs will be needed.

Electric System Planning for Extreme Weather Events: NERC Recommends Actions to Protect Reliability this Summer
June 23, 2021
Due to recent extreme weather-related power systems failures, stakeholders are examining the planning and operations practices for all electric utilities.

NERC’s FAC-008 Guidance on Facility Ratings
May 24, 2021
FAC-008 is one of the most data-intensive standards in the NERC regulatory framework. Compliance has been difficult for many utilities. Recently, FERC made public it’s intent to address serious allegations of facility ratings violations, including a lack of rigor by one utility.

NERC Issues Battery Energy Storage Systems Reliability Guidance
April 22, 2021
While NERC has recently published a reliability guideline addressing inverter-based resources generally, they are now giving more attention to the various potential uses of BESS to support effective implementation with newly released guidance.

NERC Proposes Revisions to CIP-008
March 27, 2021
NERC’s CIP-008 standard aims to mitigate reliability risks resulting from a Cyber Security Incident by specifying incident response requirements. Newly proposed revisions would augment mandatory reporting to include incidents that compromise, or attempt to compromise, a utility’s Electronic Security Perimeter (ESP) or associated Electronic Access Control or Monitoring Systems (EACMS).

Cold Weather Reliability Preparedness and Hardening
March 22, 2021
The latest weather impacts to power reliability have accelerated the need for mandatory regulatory compliance changes.

NERC Releases 2021 Compliance Monitoring and Enforcement Findings
February 8, 2021
NERC’s 2021 Compliance Monitoring and Enforcement Program reframes the previous year’s risks and their associated areas of focus. Utilities should review their compliance programs and internal controls to determine if enhancement or changes are need to maintain compliance.

NERC Proposes Revision of Pending TPL-001-5.1 Standard
January 20, 2021
NERC has recently undertaken important standards and guidance development activities related to the proliferation of inverter-based technologies such as solar and wind generation, as well as battery energy storage which is growing as an industry solution to ensure the reliability of renewable power for end-use customers.

NERC and FERC Take Action on Facilities Ratings
December 4, 2020
There has been significant work across the electric industry to improve facility ratings related processes, programs, frameworks, internal controls and best practices. Yet this continues to be a challenging area for utilities, particularly from an asset management and regulatory compliance perspective.

FERC Issues Annual Report on Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) Reliability Audits
November 17, 2020
In its 2020 Report on CIP Reliability Audits, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission found that most of the cybersecurity protection processes and procedures adopted by utilities met the mandatory CIP requirements for protecting the Bulk Electric System. However, there are areas for improvement.

NERC Prioritizes Inverter-Based Resources for Future Standards Development
October 19, 2020
As inverter-based resources found in wind and solar generation technologies continue to rapidly penetrate the U.S. power delivery system, NERC remains focused on managing the potential reliability consequences.

NERC Issues 2020 State of Reliability Report
September 22, 2020
The Report identifies areas of ongoing concern including generation reserve margins and the reliability risk from shifting the resource mix toward renewables.

NERC Issues Lessons Learned on Misoperations Due to Mixing Relay Technologies
August 13, 2020
On July 10, 2020 NERC released new Lessons Learned guidance to address situations where multiple composite protection systems have misoperated as a result of mixing protective relay technologies at the remote terminals of directional comparison blocking (DCB) schemes. This technical information will help utilities improve the reliability of the Bulk Power System.

NERC Reliability Standard PRC-024-3 Approved: Frequency and Voltage Protection Settings for Generating Resources
July 28, 2020
On July 9, 2020 NERC standard PRC-024-3 was approved, paving the way for improved protection systems in support of keeping generating resources connected during defined frequency and voltage excursions.

Summary of NERC CIP Standards Updates
June 29, 2020
FERC has released a notice of inquiry seeking comments on potential enhancements to NERC’s Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) Reliability Standards.

NERC Protection System Compliance Studies Due This Year
February 24, 2020
NERC’s PRC-027-1 standard was approved by FERC in 2018 and is set to go into effect on October 1, 2020. Utilities should begin preparing now to meet compliance requirements which include significant system studies.

NERC Compliance Assurance: Maintaining Cross Functional Data Integrity
January 21, 2020
Assuring continued power system reliability is a complex undertaking for utilities. Balancing the demands of system changes and regulatory compliance is an essential strategy for optimizing ongoing operations. Given the wide range of NERC standard families that require simultaneous data management for compliance, data integrity, data flow and data verification are critical for avoiding violations that can impact electric service to customers and communities.

NERC Reliability Report Prioritizes Power System Security Risks for Action
January 2, 2020
NERC’s 2019 ERO Reliability Risk Priorities Report identified and prioritized the major risks facing the utility industry with a particular focus on security issues.

NERC Reliability Report Prioritizes Power System Risks
November 21, 2019
Looking ahead to the many changes coming to North America’s Bulk Power System (BPS), NERC’s 2019 ERO Reliability Risk Priorities Report highlights the top issues requiring industry and regulatory attention and recommends actions for the ongoing protection of BPS reliability.

NERC Pursues Changes to Protection Relay and Control (PRC) Standards
September 24, 2019
Two Standards Authorization Requests currently being debated in the NERC stakeholder engagement process could help clarify PRC standards obligations for generator owners and operators.

NERC to Modify Standard and Develop Compliance Guidance to Accommodate Inverter-Based Generation Technologies
February 20, 2019
Renewable energy systems have dramatically changed the power generation resource mix. These new generation technologies no longer involve directly coupled rotating generators which were once standard in the industry. Now, inverters that change Direct Current (DC) electricity to the Alternating Current (AC) electricity suitable for delivery via AC transmission systems are becoming more prevalent, raising reliability…

NERC Addresses Single Points of Failure in Protection Systems Among Other FERC Concerns
October 25, 2018
As inverter-based resources found in wind and solar generation technologies continue to rapidly penetrate the U.S. power delivery system, NERC remains focused on managing the potential reliability consequences. Building on NERC’s 2019 analysis of several major power disturbances and its report outlining the risks of inverter-based renewable energy resources, the Inverter-Based Resources Task Force (IBRTF) recently issued an industry survey, the results of which will serve as a roadmap for future standards or guidance activities. Contact Us

NERC Proposes Compliance Monitoring and Enforcement Plan for 2019
September 26, 2018
This month, NERC released the first draft of its 2019 Compliance Monitoring and Enforcement Plan (CMEP) which identifies power delivery system risks and outlines compliance audit requirements for next year. The risk elements outlined in the plan include significant differences from previous years, as shown in the table below. Each NERC region must consider these risks as they develop their monitoring and audit scopes for utilities. Utilities should be prepared to be audited and implement any necessary compliance initiatives in these areas.

NERC Calls for New Approach to Reliability Planning Due to Gas Supply Disruption Risks
December 14, 2017
A recently published NERC report concludes that as reliance on natural gas to meet electric generation requirements increases, additional planning and operational measures must be considered to mitigate power system reliability risks.

Hardening Cyber Defenses at Chemical Facilities a Key Part of Federal CFATS Regulations
October 24, 2017
Federal CFATS regulations cover more than just the handling, transport and storage of dangerous chemicals. They also deal with tools and methods terrorists could use to acquire the deadly agents – such as a cyber attack.

NERC CIP-013-1 Standard for Supply Chain Risk Management
September 29, 2017
NERC has filed mandatory standard CIP-013-1 for supply chain risk management, requiring controls to mitigate cyber threats and their impact to the reliable operation of the Bulk Electric System.

NERC Identifies New Reliability Risk due to Utility Scale Solar Generation Inverter Design
June 13, 2017
NERC has released a report documenting its findings and recommendations related to reliability risks from utility scale solar generation projects with implications for PRC-024 compliance, as well as generation, interconnection and protection system technologies.

NERC Standard Extends Maintenance Program Obligations to Generators
February 3, 2014
The approval of NERC Standard PRC-005-2 extends protection system maintenance obligations to Generators and crates one comprehensive standard establishing minimum maintenance activities and maximum time intervals for protection systems and load shedding equipment affecting the bulk electric system.

Dwayne Stradford
Dwayne Stradford serves as TRC’s NERC Compliance Director in the Power Division. He is leading and coordinating TRC’s NERC compliance support services with our various power utility clients. He is an accomplished, diverse energy professional with over 30 years of engineering experience regarding real-time transmission operations, short/long term transmission planning, NERC Reliability Compliance Standards (both NERC-CIP and NERC O&P), Transmission Reliability Assurance, utility scale renewables integration, FERC Regulatory/RTO policy, and Project Management. He spent the bulk of his career (close to two decades) working for AEP but has considerable working experience in the electric utility industry as a professional consultant. He has worked with utility clients on transmission and generation related projects in all three interconnections, so he has breadth of regional BES experience throughout the entire country. Please contact Dwayne Stradford for more information.