Onshore vs. Offshore Wind
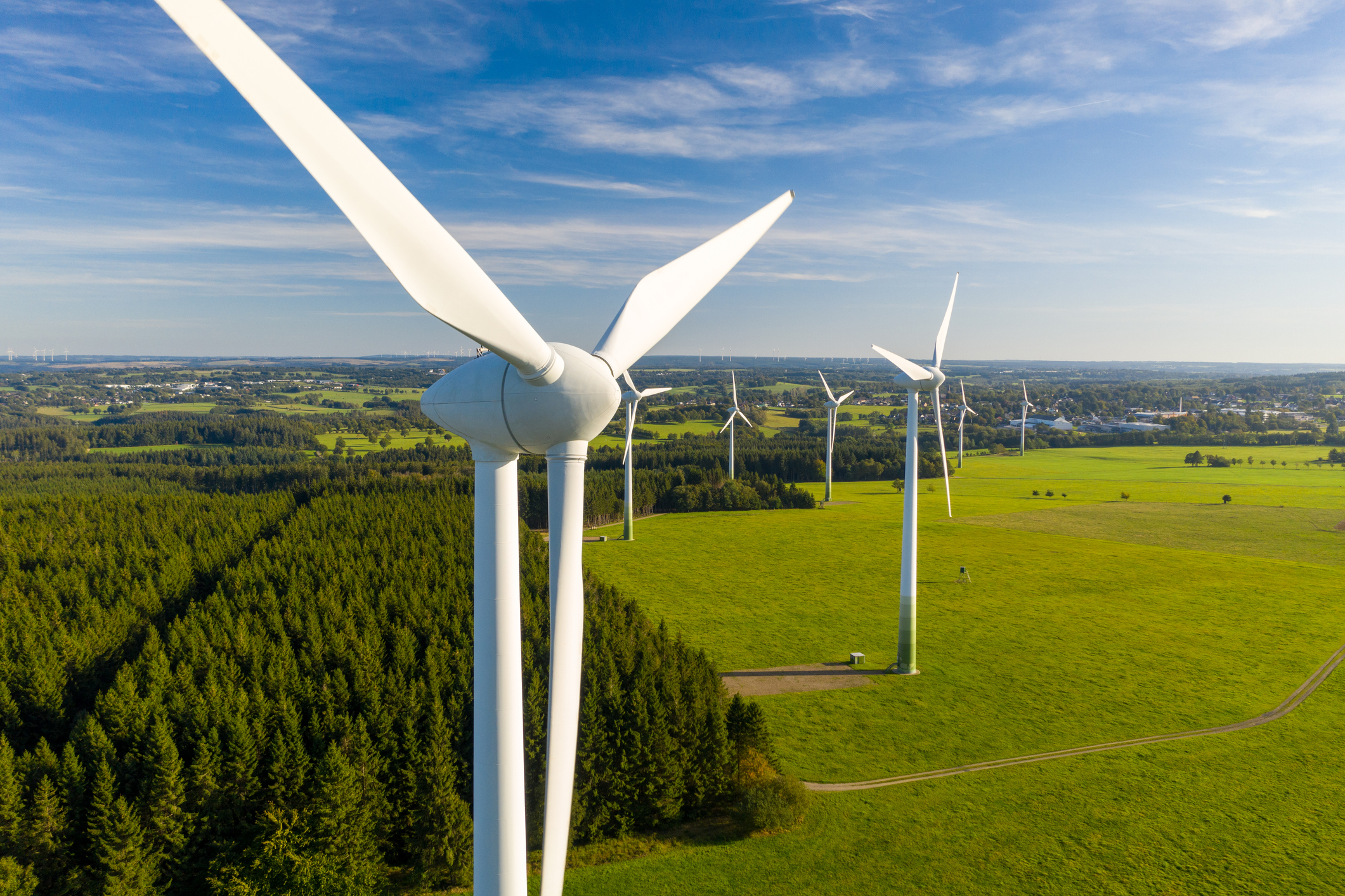
The major difference between onshore and offshore wind is the location in which the turbines are placed. Onshore wind turbines are on land, while offshore turbines are placed in a body of water. While both serve the same purpose, there are some other key differences between the two types of wind energy.
In particular, offshore wind turbines tend to encounter higher wind speeds, which leads to more energy being created. Moreover, onshore wind speeds have higher volatility, leading to greater uncertainty concerning the consistency of energy created by onshore wind turbines. Nevertheless, both types of wind power serve as important sources of renewable energy.
While offshore wind may provide a more efficient process of creating renewable energy, it comes with a high cost. The higher costs arise due to different factors such as corrosion, maintenance and other operating expenses associated with running an offshore wind turbine.
Onshore wind is a more cost-effective route when setting out to produce wind energy. Compared to offshore wind, turbines used in producing onshore wind energy are easier to install and transport, which inherently affects expenses. Additionally, it costs less to maintain onshore wind turbines due to technological advancements meant to reduce wear and tear.





 The future of wind-powered energy is bright. Experts estimate that technological advancements, among other factors, will help reduce the cost of wind energy between
The future of wind-powered energy is bright. Experts estimate that technological advancements, among other factors, will help reduce the cost of wind energy between