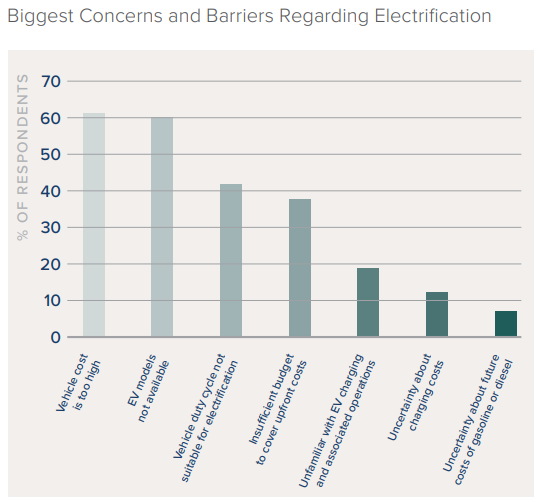
With the largest fleet operators in the US (Amazon, AT&T and others) making ambitious commitments to electrify their vehicles, the attention of the EV industry has been absorbed with the questions of when and from whom these medium and heavy duty vehicles will be coming to our streets. As we track the emergence of promising startups and watch Rivian’s production lines with bated breath, it’s unsurprising that major fleet operators’ biggest concerns with meeting their electrification goals are the availability and cost of these elusive new vehicles.
Related Services
 Biggest Concerns and Barriers Regarding Electrification
Biggest Concerns and Barriers Regarding Electrification
Garnering fewer headlines to date, another challenge troubling fleet operators is ensuring that these vehicles can be easily, affordably and safely charged.
Perceptions of the relative significance of these concerns has begun to shift, as demonstrated last fall, when the Washington Post’s Will Englund compellingly argued:
“Making America’s cars go electric is no longer primarily a story about building the cars. Against this ambitious backdrop [of fleet electrification commitments and other recent industry advancements], America’s electric grid will be sorely challenged by the need to deliver clean power to those cars.”
Quoting the former head of the New York Power Authority, Gil Quiniones (now CEO at ComEd), “We got to talk about the grid. Otherwise, we’ll be caught flat-footed.”
Through TRC’s work with utilities and fleet operators, we have seen first-hand the need for more conversations around this increasingly well-understood challenge.
While commercial fleets constitute only 3% of registered vehicles in the US and the transition to electric passenger vehicles is much further advanced, we focus here on fleets because their scale enables them to drive (pun intended) costly inefficiencies with new technology and infrastructure out of the market. This gives commercial fleets an “outsized influence” on the successful electrification of the entire transportation sector” – notably, the sector that is presently the largest contributor to greenhouse gas emissions in the US. This significance is in addition to the meaningful potential of fleet electrification to contribute to improved air quality conditions in overburdened areas full of C&I complexes, where fleet vehicles most often operate.
Given this tremendous potential to catalyze decarbonization and deliver meaningful benefits to frontline communities, we as an industry need to increase our collective focus on grid readiness for electrified fleets. Managing the grid impacts of this transformation may require megawatts of new service capacity, costly distribution system upgrades and – especially for vehicles with critical applications – microgrids or onsite storage in the event of grid outages. As we plan for and make these early investments for fleets, we’ll be paving the way for higher degrees of market penetration of passenger vehicles and other modes of transportation as well.
Preparing for the Grid Impacts of Mass Transportation Electrification
Like water, electric energy is a resource that most Americans have the privilege of “tapping into” every day, without paying much attention to the systems in place to enable that access. It’s not until we have inconvenient or even catastrophic encounters with the constraints of these systems (from PSPS events in California to the 2021 Texas power crisis) that we start asking questions. Indeed, industry analysts have warned that the early years of fleet electrification may look like “a series of very costly errors” if fleet operators, utilities and electric industry service providers don’t start talking about evolving grid needs, associated constraints and solutions to mitigate them. So let’s talk.
The first question that comes to mind for many in the industry is: how much additional electric energy will we need to replace 9.1 million barrels of oil presently consumed each day to power motor vehicles in the US?
With reference to passenger vehicles alone, analysts estimate that the US will see an increase in electricity usage of about 25% over present day levels to accommodate full electrification. Offering another perspective on this question, in light of the state of New York’s recent ban on the sale of internal combustion engine cars and trucks, projections show that by the year 2050, 14% of the state’s electric output will serve electric cars, trucks, and buses. To begin to understand how this new electric load translates into the amount of additional electric generation capacity that will be needed to accommodate it, we must also consider the questions of where and when these fleets will be plugged in.
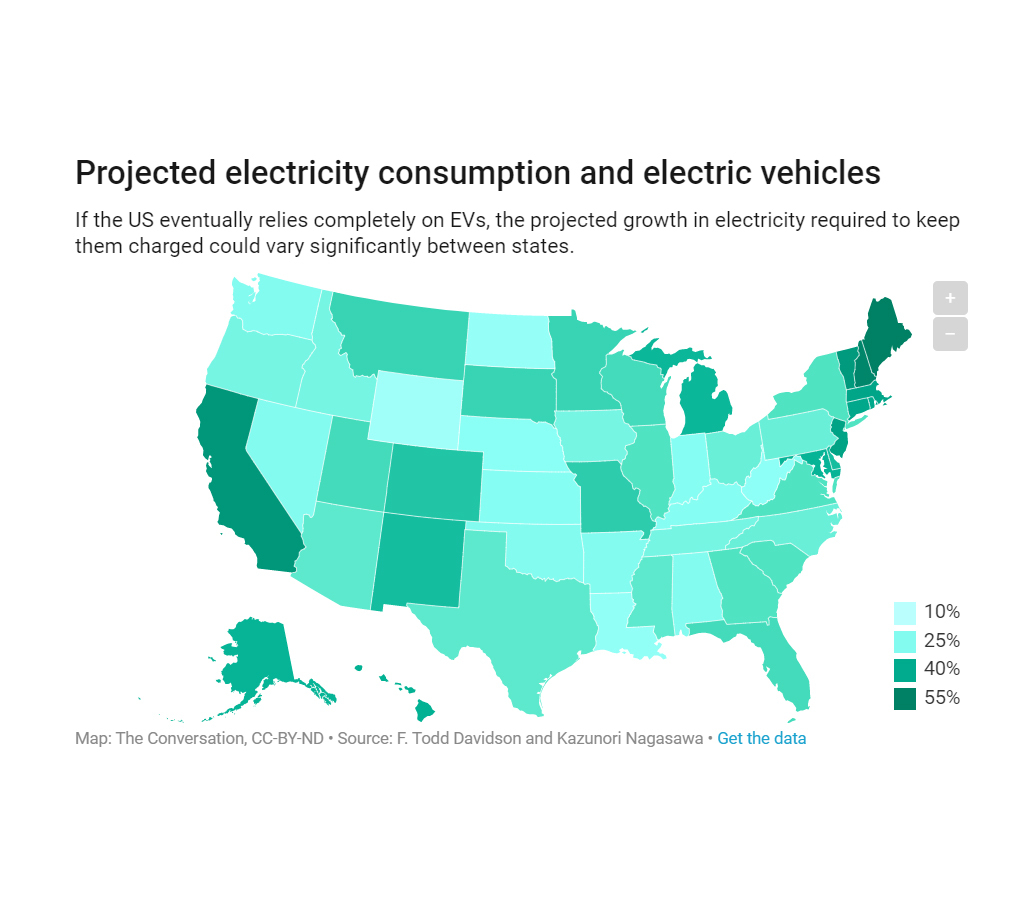
In 2018, researchers approximated the growth in electricity consumption expected to result from vehicle electrification across each US state.
A Deeper Look
Further analysis of this report – specifically, a deeper look at implications for the states of Texas and California – told “A Tale of Two Grids.” In Texas, unlike the more temperate state of California, the energy required to condition air for buildings varies considerably by season. This means that on a hot summer afternoon, roughly 50% of the Texas’ energy supply is needed to power air conditioners; so electricity suppliers must maintain many power plants to serve that “peak” load, which then remain idle for many hours of the year. This excess generation capacity presents an opportunity for the state of Texas, not afforded as generously to the state of California, where demand is more seasonally stable. If timed properly, a significant increase in load from EVs could be accommodated by existing, underutilized generating facilities.
The Promise of Time-based Rates
“If timed properly” is the crux of the issue and gets at the key question of when (what time of day) these EVs will be charging. As the Texas example demonstrates, charging habits that coincide with the existing, natural peak of the local power system could result in the costly buildout of even more underutilized generating plants. To avoid this “when it rains, it pours” scenario for the power grid – and for all electricity consumers paying for these investments –, a key piece of the solution lies in well-designed and responsibly enacted time-based electric rates.
Time-based rates allow electric utilities and other power providers to charge less for (and thereby, incentivize) customers’ consumption that is aligned with the needs of the power system, and to charge more (as a disincentive) at times of the day, week, or year when that consumption jeopardizes grid reliability or drives up the system owners’ and operators’ costs of providing service. Certain time-based rate structures have existed for over a decade, but the deployment of advanced (smart) metering infrastructure over the past several years has contributed to their increased prevalence and sophistication. While these rapidly evolving rate structures support utilities’ abilities to manage the grid impacts of new and existing load at the lowest possible cost to ratepayers, they also expose customers to new risks. Customers become responsible for responding to these market signals and run the risk of an inverse benefit if they are unable to conform their consumption or behavior to the needs of the grid (i.e. operate “off-peak”). Presently, utilities often offer time-based rates on an opt-in basis, but they are becoming default or even required in certain regions, especially for EV charging applications, making it important to keep these risks front-of-mind while contemplating the promising role of time-based rate structures in a responsible transition to electrified transportation.
To conclude the tale of Texas’ and California’s grids, it’s important to note that the state of California alone has 16 different climate zones, and a wealth of information has come to light over the past year about the intricacies of Texas’ grid. This is to say that there is tremendous intrastate variability with respect to electric power systems. To this point, tellingly, the same phrase – “A tale of two grids” – is used by grid operators in New York to characterize the state’s own electric power system. In this case, one of the most constrained transmission lines in the country connects the rural and Rust Belt northwestern region of the state with the metropolitan southeast – in effect, two grids which vary significantly by load size and type, as well as by the cleanliness of the local energy generators. This point is made to demonstrate the regional, local, and even hyper-local nature of the issues at the root of transportation electrification – all of which underscore the level of support and resources needed by national fleet operators seeking consistent solutions that can be applied at scale.
Finally, it’s crucial to recall that fleet electrification efforts center on these owners’ and operators’ commitments to decarbonization. These goals will not be achieved by replacing oil-powered cars with coal-powered electric cars.
And as the Flint, Michigan crisis demonstrated with respect to water quality – to ensure comprehensive power quality for EV charging applications, we must look beyond cleanliness of the source (i.e., generation technology) to consider the impacts of distribution infrastructure as well. Specifically for the electric grid, this means frequency and voltage regulation. As distributed energy resources (DERs) (including EVs and their supply equipment) continue to proliferate on the grid, this presents a challenge to distribution utilities and grid operators tasked with ensuring that increasingly irregular and newly bidirectional energy flows are safely accommodated and do not present reliability issues for end users. Utilities are making tremendous investments in transmission and distribution (T&D) infrastructure, and much more is needed. Fortunately, in light of FERC Order No. 2222 and related market advancements, customers – including fleet owners and operators – are empowered to support their utilities in solving these problems (and be compensated for this support) via distributed energy storage resources and other inverter-based technologies capable of managing fluctuations in voltage and frequency. Again, early coordination among end users and their utilities will be key in finding economical solutions to these problems before disruptive constraints are encountered.

Collaborating to Ensure Grid Readiness
We as an industry need to initiate more discussions and planning around the grid impacts of fleet electrification – which will depend not only on where, but also when these vehicles are charged – and collaborate on solutions that keep resource quality at the center. While electricity providers and regulators plan for what this means on the system level – investments in additional capacity, T&D system upgrades, etc. – it will be up to fleet owners and operators to determine how the broader needs and challenges outlined here translate to their individual facilities and to start those conversations with utilities and solutions providers. These conversations will need to take place years in advance of expected deployment (or ASAP) to account for utilities’ resource planning and regulatory timeframes. We have the power to determine whether the early years of fleet electrification look like a series of costly failures or an intentional, collaborative, just, and transformative effort to decarbonize the highest GHG-emitting sector of the US. While this transition didn’t start with fleets, fleets present an opportunity to accelerate this transition and turn a trickle to a waterfall.
Tune Into our Podcast to Learn More
TRC continues this important discussion with this episode of TRC Energy Talks on the Doers, the Dollars, and the Double-Edged Sword of Transportation Electrification, covering opportunities for TE in the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, justice concerns with the TE rollout to date, and – of course – discussion of grid impacts of TE and how they can be proactively managed and mitigated.
TRC’s Advanced Energy Practice offers advisory and consulting services that help our clients achieve a clean and equitable energy future for the communities they serve. We support clients with decarbonization, resiliency, and electrification strategy for the transportation, building, and industrial sectors. To learn more, contact advancedenergy@trccompanies.com.
Embrassez le changement
Collaborez avec les praticiens testés de TRC



 Biggest Concerns and Barriers Regarding Electrification
Biggest Concerns and Barriers Regarding Electrification