The compound 6PPD (short for 1,4-Benzenediamine, N-(1,3-dimethylbutyl)- 21 N’-phenyl-; CAS #793-24-8) is an antioxidant and antiozonant that prevents degradation of rubber compounds caused by their exposure to oxygen, ozone and temperature fluctuations. 6PPD is widely used in the tire manufacturing industry to help tires resist degradation and cracking and promote product longevity and performance.
Typical automobile or truck tires endure significant abrasive forces resulting in in fragments called tire and road wear particles (TRWP). TRWP include material from both tire treads and road surfaces, and are transported into various environmental media, largely through stormwater runoff. Research conducted by Unice et. al estimates 16% of TRWP migrate to the soil, 18% to surface water, 16% to sediment, 2-5% to estuaries and 2% to the atmosphere. The remaining 19% are either retained in the road surface (1%) or removed through stormwater management (18%). The 6PPD within the TRWP is carried via stormwater and exposed to ozone, producing a by-product called 6PPD-quinone (6PPD-Q). 6PPD-Q is frequently transported directly to natural receiving waters and vulnerable aquatic ecosystems.
Related Services
Impact on Aquatic Environments
Environmental impacts from 6PPD and 6PPD-Q are an emerging area of study (the Interstate Technology Regulatory Council or ITRC has assembled a team on the topic), and the collective understanding of the toxicological impacts of 6PPD and 6PPD-Q is still unfolding. However, a study conducted on the toxicological effects of 6PPD-Q by Tian et al. out of Washington-Tacoma University in 2020 revealed that juvenile Coho Salmon, one of five Pacific salmon species, had a staggeringly low 6PPD-Q concentration that would result in a 50% mortality of the exposed population (LC50 value) of 95 ng/L.
The same study further notes that the concentration of 6PPD-Q detected in roadway runoff in the Seattle area was 800 ng/L to 1,900 ng/L—an order of magnitude greater than the LC50 of 95 ng/L for Coho Salmon that are found in waterways in Washington State. In a healthy stream, less than 1% of Coho Salmon die before spawning, but in these affected areas 40-90% of the fish population died prior to spawning, putting the species at a significant risk. As a result, 6PPD-Q has been attributed to the high levels of fish kills that occurred in Washington state in small streams following rain events.
The United States Endangered Species Act defines evolutionarily significant units (ESUs) of species if they (1) are reproductively isolated from other populations of the same species and (2) represent an important component in the evolutionary process of the species. One ESU of the Coho Salmon is listed as “endangered” and three ESUs are listed as “threatened” under the Endangered Species Act. This designates Washington as a vulnerable area for this contaminant, prompting a great demand for sampling and stormwater mitigation efforts.
Toxicology
The 6PPD-Q LC50 of 95 ng/L for Coho Salmon is incredibly low. For context, several LC50 values for other contaminants are provided below for comparison. As illustrated, these values are generally orders of magnitude greater that the LC50 for 6PPD-Q.
Example Aquatic Species LC50 Values for Other Contaminants
|
Contaminant |
Species |
LD50 |
| Fenvalerate | Atlantic Salmon | 1,200 ng/L |
| Thiobencarb | Chinook Salmon | 760,000 ng/L |
| Dinocap (fungicide) | Rainbow Trout | 15,000 ng/L |
| Ozone | Rainbow Trout | 9,300 ng/L |
Follow up aquatic studies conducted by Lo et. al looked at the toxicological impact of 6PPD-Q on other species and reported the LC50 values, which further highlights the sensitivity of Coho Salmon to 6PPD-Q.
|
Species |
LD50 |
| Juvenile Chinook Salmon | >67,306 ng/L |
| White Spotted Char | 510 ng/L |
| Japanese Medaka | >34,000 ng/L |
Toxicological Impact for Humans
6PPD and 6PPD-Q can also pose risks to human populations.
6PPD is a known skin sensitizer, can cause allergic contact dermatitis in sensitive individuals and is designated a category 1B reproductive toxicant by the European Chemical Agency. A category 1B toxicant is defined as a suspected toxicant based on evidence from animal or limited human studies.
6PPD-Q has been detected in human urine, with pregnant women exhibiting higher concentrations of both 6PPD and 6PPD-Q. This suggests that it is being ingested, absorbed, or inhaled from the surrounding environment. However, 6PPD-Q’s toxicity in humans is, at this point, mostly unknown. It is predicted to cause oxidative stress like other quinones. In a study by Fang et. al, it caused liver toxicity in mice when they were given oral doses at high levels.
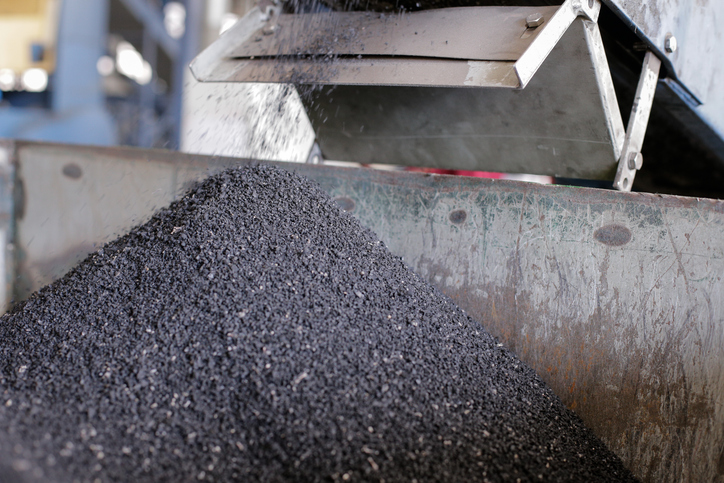

Reevaluating Tire Reuse
The rise of tire recycling has recently been viewed as a positive, sustainable waste material reuse option. Tires have been ground into rubber crumb and used to create synthetic turf, playground floors, road banks, etc. However, with respect to 6PPD-Q, the reuse of tire material may become a growing concern for the surrounding ecosystem, especially in vulnerable areas near sensitive fish species. Due to the low 6PPD-Q LC50 values determined for various aquatic organisms, this tire material reuse combined with typical wear and tear of tires on active roadways could lead to significant negative impacts (and potentially extinctions) of vital, culturally significant aquatic species.

Big Picture
Currently, source reduction as a method of contaminant control is unfortunately not an option. The tire manufacturing industry is researching potential 6PPD substitute compounds, but no viable alternatives are presently available. An alternative component would have to provide the same or higher level of degradation and cracking prevention to avoid posing significant safety risks.
To protect aquatic environments and humans from 6PPD and 6PPD-Q, stormwater could be treated to remove contaminants before they reach natural receiving waters. Potential treatment methods include such as sand filters, infiltration basins and trenches, dry ponds, bioretention, dry and wet ponds, constructed wetlands, filter strips, swales, wet vaults and underground sedimentation practices.
What Can Be Done?
The best management practices for preventing 6PPD-Q from entering nearby streams include street sweeping, flow control through mitigation techniques and treatment. Such mitigation techniques include the implementation of green stormwater infrastructure to control the flow and absorb and filter the 6PDD-Q before it reaches the nearby streams. As more research is conducted in identifying an alternative for 6PPD in tire manufacturing there may be opportunities to target the source of the problem but currently no known alternatives are available. The US Tire Manufacturing Association (USTMA) and the Tire Industry Project are focusing their efforts on re-evaluating the tire manufacturing process to eliminate the need for 6PPD.
TRC is Engaged in Finding Solutions
TRC actively participates on the Interstate Technology and Regulatory (ITRC) Tire Anti-Degradants (6PPD) team to track the toxicity and fate & transport risks posed by 6PPD-Q. We are prepared to assist you with your 6PPD and 6PPD-Q related questions. For more information, please contact our expert below.

S’adapter au
changement
Collaborez avec les praticiens testés de TRC