In response to a directive from the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC), the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) has launched an Inverter-Based Resource (IBR) Registration Initiative to address a critical reliability gap. If IBRs connected to the Bulk Power System (BPS) are unregistered and therefore are not subject to NERC Reliability Standards this reliability gap will be perpetuated with significant risk to reliability. The initiative will ensure that all materially impactful IBRs are identified, registered and compliant with NERC’s mandatory reliability standards by 2026.
Status of IBR Registration Effort
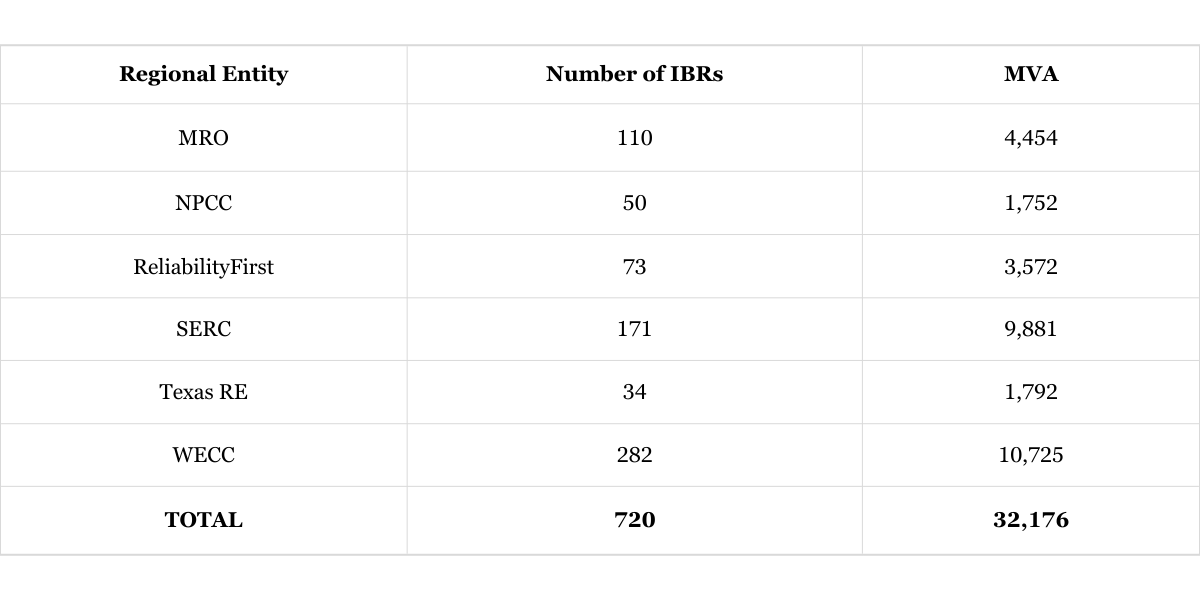
As of May 15, 2025, NERC has identified the following IBR Facility totals in each region as follows:
NERC’s IBR Registration Program is a critical step toward ensuring grid reliability as inverter-based resources become more prevalent. IBR owners and operators must act promptly to assess the applicability of the registration criteria and should respond to the NERC/Region Requests for Information (RFIs). Next, they must complete their respective NERC registration and prepare for compliance with NERC’s mandatory standards. The initiative is supported by extensive outreach efforts and explanatory resources to ease the transition into the regulated framework. IBR owners must develop compliance programs to meet the requirements of the following currently applicable mandatory NERC standards:
- PRC-024-4 – Frequency and Voltage Protection Settings
- Applies to Type 1 and Type 2 wind resources and synchronous condensers
- Ensures protection settings do not interfere with grid reliability
- Requires coordination of frequency and voltage trip settings to prevent unnecessary disconnection during system disturbances
- PRC-029-1 – Ride-Through Requirements for IBRs
- Mandates that IBRs remain connected during voltage and frequency excursions
- Addresses “ride-through” capability to prevent cascading outages
- Critical for maintaining grid stability during transient events
- MOD-032 and MOD-033 – Data Submission and Model Validation
- Requires IBR owners to submit accurate modeling data for planning and interconnection studies
- Ensures that dynamic models reflect actual performance
- Supports system planners in evaluating reliability impacts of IBRs
- FAC-001 and FAC-002 – Facility Interconnection Requirements
- Govern coordination between IBRs and transmission planners and operators
- Requires documentation and review of interconnection reliability impacts
- Ensures safe and reliable integration of IBRs into the Bulk Power System
- CIP Standards – Cybersecurity Compliance
- Includes CIP-002 through CIP-014, covering asset identification, access controls, incident response and supply chain risk management
- May apply depending on the IBR’s physical and cyber security classification and system impact
Key Actions Required of IBR Owners
IBR project owners must determine whether their facilities meet the criteria for Category 2 Generator Owner (GO) or Generator Operator (GOP):
- Gross Aggregate Nameplate Capacity ≥ 20 MVA
- Connection Voltage greater than 60 kV
To support this effort, NERC and the Regional Entities RFIs require submission of:
- One-line diagrams
- Generator operating agreements
- Generator interconnection agreements
- GO/GOP asset verification forms
Next Steps
To ensure compliance and readiness, IBR owners should:
- Review applicable NERC standards for IBRs
- Assess their facility protection settings and ride-through capabilities.
- Submit accurate modeling data to planning authorities.
- Prepare for compliance with cybersecurity, operations and planning standards
- Stay informed on evolving standards and participate in NERC webinars and outreach
Resources
TRC Can Help
TRC’s approach to power system development integrates regulatory requirements, industry best practices and operational goals. Our deep understanding of NERC compliance enables us to support both public and private utility clients in navigating evolving standards.
We offer:
- Strategic planning and design of compliance programs
- Technology solutions tailored to regulatory and operational needs
- Expertise in implementing programs that meet financial, technical and scheduling goals
Ongoing engagement with regulatory developments to keep your systems ahead of the curve. This regulatory update is a part of TRC’s commitment to helping utility clients stay informed and prepared for changes that impact electric reliability and regulatory compliance.